Define fixed exchange rate. How is the exchange rate determined in a flexible exchange rate system?
CBSE OUTSIDE DELHI RE- PAPER SET 2 2018
Fixed exchange rate (also known as pegged exchange rate) is determined by the government and government has complete control over it. Under a fixed exchange rate, the exchange rate remains fixed as determined by the government.
Equilibrium Exchange Rate:
Under a flexible exchange rate regime, the exchange rate is determined by the forces of demand and supply. Demand for foreign exchange arises from the need to make payments in foreign exchange. Demand for foreign exchange varies inversely with the foreign exchange rate. As the foreign exchange rate rises, the demand for foreign exchange falls and vice versa. Supply of foreign exchange arises from the receipts of foreign exchange.
The supply of foreign exchange rate varies directly with the foreign exchange rate. As foreign exchange rate rises, the supply of foreign exchange rises and vice versa.
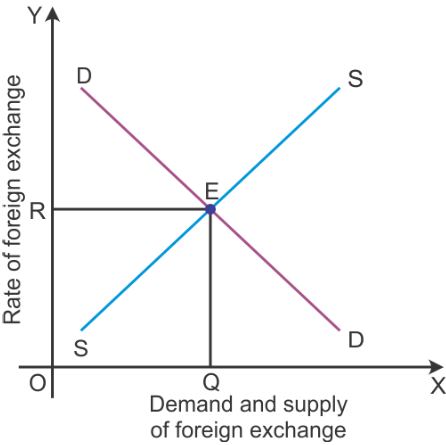
Equilibrium exchange rate is determined at the point where the demand for foreign exchange is equal to the supply of foreign exchange. Graphically, it is determined at the point where the demand curve for foreign exchange intersects the supply curve of foreign exchange.
According to the graph, the equilibrium is determined at Point E, where the demand curve DD intersects the supply curve SS. Here, the equilibrium exchange rate is OR and the equilibrium quantity of foreign exchange is OQ.
Equilibrium Exchange Rate:
Under a flexible exchange rate regime, the exchange rate is determined by the forces of demand and supply. Demand for foreign exchange arises from the need to make payments in foreign exchange. Demand for foreign exchange varies inversely with the foreign exchange rate. As the foreign exchange rate rises, the demand for foreign exchange falls and vice versa. Supply of foreign exchange arises from the receipts of foreign exchange.
The supply of foreign exchange rate varies directly with the foreign exchange rate. As foreign exchange rate rises, the supply of foreign exchange rises and vice versa.
Equilibrium exchange rate is determined at the point where the demand for foreign exchange is equal to the supply of foreign exchange. Graphically, it is determined at the point where the demand curve for foreign exchange intersects the supply curve of foreign exchange.
According to the graph, the equilibrium is determined at Point E, where the demand curve DD intersects the supply curve SS. Here, the equilibrium exchange rate is OR and the equilibrium quantity of foreign exchange is OQ.

Download our appand get started for free
Experience the future of education. Simply download our apps or reach out to us for more information. Let's shape the future of learning together!No signup needed.*
Similar Questions
- 1View SolutionIn the above example, if exports change to X = 100, find the change in equilibrium income and the net export balance.
- 2View SolutionIndian investors borrow from abroad. Answer the following:
- In which sub-account and on which side of the Balance of Payments Account will this borrowing be recorded? Give reason.
- Explain what is the impact of this borrowing on exchange rate.
- 3View SolutionWhy does the demand for foreign currency fall and supply rises when its price rises? Explain.
- 4Calculate:View Solution
- Operating Surplus.
- Domestic Income.
$(₹$ in crores$)$ $(i)$ Compensation of employees $2,000$ $(ii)$ Rent and interest $800$ $(iii)$ Indirect taxes $120$ $(iv)$ Corporation tax $460$ $(v)$ Consumtion of fixed capital $100$ $(vi)$ Subsidies $20$ $(vii)$ Dividend $940$ $(viii)$ Undistributed profits $300$ $(ix)$ Net factor income to abroad $150$ $(x)$ Mixed income $200$ - 5View SolutionThe following figures are based on BoP accounts:
Calculate:S.No.(₹ in crores)1.Import of goods.8002.Export of goods.5503.Import of services (Banking, Shipping, Insurance, Tourism, etc.)504.Export of services (Banking, Shipping, Insurance, Tourism, etc.)1505.Unilateral transfers from rest of the world (Gifts, Aids, etc.)1006.Unilateral transfers to rest of the world (Gifts, Aids, etc.)807.Capital receipts (Loan from foreigners, Sale of assets to foreigners, Receipt of capital from foreigners).2008.Capital Payments (Loans to foreigners, Buying of assets from foreigners, Payment of capital to foreigners).70- Balance of Trade.
- Balance of Payments on Current Account.
- Balance Payments on Capital Account.
- Balance of Payments.
- 6View SolutionDistinguish:
- Between current account and capital account.
- Between autonomous transactions and accommodating transactions of balance of payments account.
- 7View SolutionDiscuss briefly the meanings of:
- Fixed Exchange Rate.
- Flexible Exchange Rate.
- Managed Floating Exchange Rate.
- 8View SolutionSuppose C = 100 + 0.75Y D, I = 500, G = 750, taxes are 20 percent of income, X = 150, M = 100 + 0.2Y . Calculate equilibrium income, the budget deficit or surplus and the trade deficit or surplus.
- 9View SolutionGive the meaning of 'foreign exchange' and 'foreign exchange rate'. Giving reason, explain the relation between foreign exchange rate and demand for foreign exchange.
- 10View SolutionExplain the distinction between autonomous and accommodating' transactions in balance of payments. Also explain the concept of balance of payments 'deficit' in this context.
