How is the exchange rate determined under a flexible exchange rate regime?
Flexible exchange rate is determined by the forces of supply and demand in the international market. And the equilibrium exchange rate is determined at a level where demand for foreign exchange is equal to the supply of foreign exchange.Sources of demand for foreign exchange:
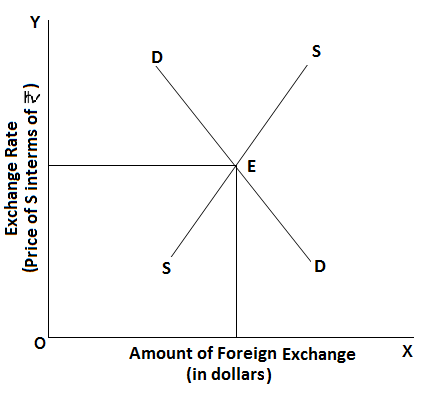 In the figure, the equilibrium exchange rate i.e., E.
In the figure, the equilibrium exchange rate i.e., E.
- Payment of international loans.
- Gifts and grants to rest of the world.
- Export to the rest of the world.
- Direct foreign investment.
- Direct purchase of goods and services by the non-residents in the domestic market.
 In the figure, the equilibrium exchange rate i.e., E.
In the figure, the equilibrium exchange rate i.e., E.Download our appand get started for free
Experience the future of education. Simply download our apps or reach out to us for more information. Let's shape the future of learning together!No signup needed.*
Similar Questions
- 1View SolutionWhat is the difference between direct tax and indirect tax? Explain the role of government budget in influencing allocation of resources.
- 2View SolutionWhat is government budget? Explain how taxes and subsidies can be used to influence allocation of resources.
- 3View SolutionExplain the concept of 'deflationary gap'. Also, explain the role of 'margin requirements' in reducing it.
- 4View SolutionConsider an economy described by the following functions: C = 20 + 0.80Y, I = 30, G = 50, TR = 100.
- Find the equilibrium level of income and the autonomous expenditure multiplier in the model.
- If government expenditure increases by 30, what is the impact on equilibrium income?
- If a lump-sum tax of 30 is added to pay for the increase in government purchases, how will equilibrium income change?
- 5View SolutionIn an economy, if initial investments are increased by ₹ 100 crores, discuss the working of investment multiplier presuming marginal propensity to consume is 0.8.
- 6View SolutionExplain the meaning of the following:
- Revenue deficit.
- Fiscal deficit.
- Primary deficit.
- 7View SolutionSuppose that for a particular economy, investment is equal to 200, government purchases are 150, net taxes (that is lump-sum taxes minus transfers) is 100 and consumption is given by C = 100 + 0.75Y,
- What is the level of equilibrium income?
- Calculate the value of the government expenditure multiplier and the tax multiplier.
- If government expenditure increases by 200, find the change in equilibrium income.
- 8View SolutionWhat is government budget? Explain the role of government budget in influencing allocation of resources in the economy.
- 9View SolutionIn the above question, calculate the effect on output of a 10 percent increase in transfers, and a 10 percent increase in lump-sum taxes. Compare the effects of the two.
- 10View SolutionHow is tax revenue different from administrative revenue?
