(પાણીની ઘનતા : $10^{3}\, kg / m ^{3}$).
The nature of flow is determined by Reynolds Number.
\(R _{ e }=\frac{\rho vD }{\eta}\)
\([\rho \rightarrow\) density of fluid ;
\(\eta \rightarrow\) coefficient of ;
\(v \rightarrow\) velocity of flow ;
\(D \rightarrow\) Diameter of pipe\(]\)
From NCERT
If \(R _{ e }<1000 \quad \rightarrow\) flow is steady
\(1000< R _{ e }<2000 \rightarrow\) flow becomes unsteady
\(R _{ e }>2000 \rightarrow\) flow is turbulent
\(R _{ e \text { initial }}=10^{3} \times \frac{0.18 \times 10^{-3}}{\pi \times\left(0.5 \times 10^{-2}\right)^{2} \times 60} \times \frac{1 \times 10^{-2}}{10^{-3}}\)
\(=382.16\)
\(R _{ efinal }=10^{3} \times \frac{0.48 \times 10^{-3}}{\pi \times\left(0.5 \times 10^{-2}\right)^{2} \times 60} \times \frac{1 \times 10^{-2}}{10^{-3}}\)
\(=1019.09\)
Download our appand get started for free
Similar Questions
- 1પાણીની સપાટીથી વસ્તુને $2\, km$ ઊંડાઇએ રાખતા તેના કદમાં થતો ફેરફાર $\frac{\Delta V }{ V }=1.36\, \%,$ હોય તો તેના કદ પ્રતિબળ અને કદ વિકૃતિ નો ગુણોત્તર કેટલો થાય?[પાણીની ઘનતા $=1000\, kg m ^{-3}$ અને $\left. g =9.8 \,ms ^{-2} .\right]$View Solution
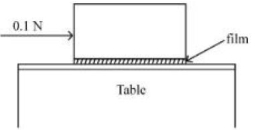
- 2આકૃતિમાં દર્શાવ્યા અનુસાર $0.20\,m ^2$ ના બેઝ (તળીયા) નું ક્ષેત્રફળ ધરાવતા એક ધાતુના ચોસલાને ટેબલ ઉપર મૂકવામાં આવેલ છે. એક $0.25\,mm$ ની પ્રવાહીની કપોટીને બ્લોક (ચોસલું) અને ટેબલની વચ્યે દાખલ કરવામાં આવે છે. બલોકને $0.1\,N$ ના સમક્ષિતિજ બળ વડે ખેંચવામાં આવે છે અને તે અચળ ઝડપથી ગતિ કરે છે. જો પ્રવાહીની સ્નિગ્ધતા $5.0 \times 10^{-3}\;Pa-s$ હોય તો બ્લોકની ઝડપ (લગભગ) $...........\times 10^{-3}\,m / s$ હશે.View Solution
- 3View Solutionતળાવમાં તરતી બોટમાં એક લોખંડનો ટુકડો રાખેલ છે. જો આ ટુકડાને તળાવમાં નાખવામાં આવે તો પાણીનું લેવલ
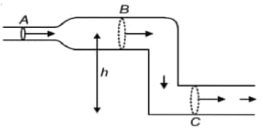
- 4આકૃતિમાં દર્શાવ્યા મુજબ ચેનલમાંથી પાણીનું વહન થઈ રહ્યું છે. (શિરોલંબ સમતલમાં રહેલી) ત્રણ ભાગો $A, B$ અને $C$ દર્શાવેલા છે. $B$ અને $C$ વિભાગ આડછેદનું સમાન ક્ષેત્રફળ ધરાવે છે. જો $P_A, P_B$ અને $P_C$ એ અનુક્રમે $A, B$ અને $C$ પરના દબાણો હોય તોView Solution
- 5View Solutionનળાકાર નળીમાં ધટ્ટ પ્રવાહીનું વહન થાય છે.પ્રવાહીનો વેગ કઇ આકૃતિ મુજબ હોય .
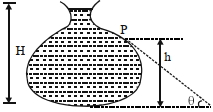
- 6$\rho$ ઘનતાના પ્રવાહીથી ભરેલા પાત્રનો શિરોલંબ આડછેદ આકૃતિમાં દર્શાવેલ છે. દર્શાવેલ દિવાલના બિંદુ $P$ પર એકમ આડછેડના ક્ષેત્રફળ દીઠ લાગતું લંબ બળ કેટલું હશે?View Solution
- 7$1 \,\mu m$ ત્રિજ્યા ધરાવતું પાણીનું એક ટીપું જ્યાં ઉત્પ્લાવક બળ ના પ્રવર્તતું હોય તેવી જગ્યાએ પડે છે હવા માટે શ્યાનતા ગુણાંક $1.8 \times 10^{-5} \,Nsm ^{-2}$ અને તેની ધનતા પાણીની ધનતા $\left(10^{6} \,gm ^{-3}\right)$ કરતા અવગણી શકાય તેટલી છે. પાણીના ટીપાંનો અન્ય (ટર્મિનલ) વેગ............ $\times 10^{-6}\,ms ^{-1}$ હશે. (ગુરુત્વકર્ષી પ્રવેગ =$10$ $ms$ ${ }^{-2}$ લો.)View Solution
- 8View Solutionવિધાન : પ્રવાહમાં જ્યારે દબાણ વધુ હોય ત્યાં વેગ ઓછો હોય અને ઊલટું પણ (દબાણ ઓછું અને વેગ વધુ)
કારણ : બર્નુલીના નિયમ મુજબ આદર્શ પ્રવાહીના વહન માટે એકમ દળમાં રહેલ કુલ ઉર્જા અચળ હોય.
- 9$A $ આડછેદવાળી ટાંકીમાં ${H_1}$ ઊંચાઇ સુઘી પાણી ભરેલ છે. તળિયે $a$ આડછેદવાળું છે.તો પાણીની ઊંચાઇ ${H_1}$ માંથી ${H_2}$ $(h_1>h_2)$ થવા માટે કેટલો સમય લાગશે?View Solution
- 10View Solutionનળાકાર નળીમાં ધટ્ટ પ્રવાહીનું વહન થાય છે.પ્રવાહીનો વેગ કઇ આકૃતિ મુજબ હોય .
