$KOH$ના આલ્કોહોલિક દ્રાવણનો ઉપયોગ શું થાય છે?
IIT 1990, Medium
c
(c) \(C{H_3} - C{H_2} - Br + \mathop {KOH}\limits_{{\rm{alk}}}\,\, \xrightarrow{Dehydrohal ogenation} \,\,C{H_2} = C{H_2} + KBr + {H_2}O\)
(c) \(C{H_3} - C{H_2} - Br + \mathop {KOH}\limits_{{\rm{alk}}}\,\, \xrightarrow{Dehydrohal ogenation} \,\,C{H_2} = C{H_2} + KBr + {H_2}O\)
In alcoholic \(KOH\) alkoxide ions \((R{O^ - })\) are present which is a strong base. They abstract proton from ?-carbon of alkyl halide and favours elimination reaction
\(\mathop {ROH}\limits_{{\rm{Alcohol}}} + KOH \to \mathop {ROK + {H_2}O}\limits_{{\rm{Potassium \,alkoxide}}} \)
\(ROK \to \mathop {R{O^ - }}\limits_{{\rm{Alkoxide \,ion}}} + {K^ + }\)
\(R{O^ - } + H - \mathop {C{H_2}}\limits^\beta - \mathop {C{H_2}}\limits^\alpha - Br \to ROH + C{H_2} = C{H_2} + Br\)
Download our appand get started for free
Experience the future of education. Simply download our apps or reach out to us for more information. Let's shape the future of learning together!No signup needed.*
Similar Questions
- 1$1$-બ્યુટાઈનનું ઓક્સિમરક્યુરેશન $(HgSO_4 + H_2SO_4) $ દ્વારા કઈ નીપજ મળશે ?View Solution
- 2પ્રક્રિયામાં $'X' $ શું છે ?View Solution
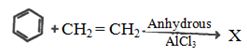
- 3નીચે હેકઝેન ના ચાર સમઘટકીય બંધારણ આપેલા છે નીચે આપેલા નામો માં કયું પાંચમો સમઘટક શોધશે ?View Solution
$CH_3CH_2CH_2CH_2CH_2CH_3$ $(CH_3)_3 CCH_2CH_3$
$(CH_3)_2CHCH_2CH_2CH_3$ $(CH_3)_2CHCH(CH_3)_2$ - 4View Solutionઆલ્કેનનું હેલોજિનેશન એ કઇ ક્રિયાવિધિનું ઉદાહરણ છે ?
- 5View Solutionક્લોરોપ્રિન બનાવવા માટે એસિટિલિનનુ ડાયમરાઈઝેશન કરવા જરૂરી ઉદ્દીપક .... છે.
- 6આપેલ પ્રક્રિયામાં નીપજ $Z$ જણાવો.View Solution
$CH_3 CH_2 CH=CH_2 \xrightarrow{{HBr/{H_2}{o_2}}}\,Y\,\xrightarrow{{{C_2}{H_5}ONa}}Z$
- 7પદાર્થનું અણુસૂત્ર છે તો $X$ પદાર્થની સંખ્યા કેટલી થાય ?View Solution
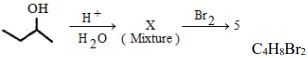
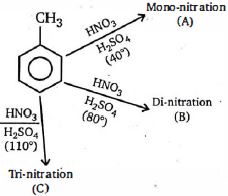
- 8View Solutionનીચેની દરેક પ્રક્રિયામાં કેટલી નિપજો ટોલ્યુઇનમાંથી રચાયેલા માટે સક્ષમ છે
- 9બ્યુટ-$1$-આઇનમાં એસિડિક હાઇડ્રોજનની સંખ્યા...... છે.View Solution
- 10પ્રક્રિયા $C_6H_6 \rightarrow C_6H_5CH_3$ …….View Solution
