$(1)$ $C{H_3} - \mathop {CH}\limits^ \bullet C{H_3}$
$(2)$ (ચિત્ર.)
$(3)$ $\mathop {C{H_2}}\limits^ \bullet - CH{(C{H_3})_2}$
$(4)$ $\mathop {C{H_2}}\limits^ \bullet - C{H_3}$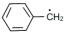
\((1)\) \(C{H_3} - \mathop {CH}\limits^ \bullet C{H_3}\)
\((2)\) (fig.)
\((3)\) \(\mathop {C{H_2}}\limits^ \bullet - CH{(C{H_3})_2}\)
\((4)\) \(\mathop {C{H_2}}\limits^ \bullet - C{H_3}\)
The stability of free radicals is mostly affected by the factors like resonance, hyperconjugation and inductive effect. In compound \( (II)\), there is high resonance effect due to which it is highly stable than other three compounds. The effect of hyperconjugation is directly proportional to the number alpha hydrogen. So, compound \(I\) has six alpha hydrogen atoms, compound \(III \) has one alpha hydrogen atom and compound \(IV\) has three alpha hydrogen atoms. Therefore, the order is \(II > I > IV > III.\)
Download our appand get started for free
Similar Questions
- 1$H - C \equiv C\mathop {-} \limits^a C \equiv C\mathop {-} \limits^b C{H_3}$View Solution
$a$ અને $b$ ની બંધ લંબાઈની તુલના કરો
- 2View Solutionએન્થ્રેસીન માટે કેટલા સંસ્પંદન બંધારણ છે?
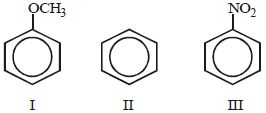
- 3નીચેના સંયોજનોમાં $(I-III)$ , ઇલેક્ટ્રોન અનુરાગી વિસ્થાપન પ્રક્રિયા તરફ પ્રતિક્રિયાશીલતાનો યોગ્ય ક્રમ છેView Solution
- 4બેન્ઝિનમાં $C-C$ બંધ લંબાઈ ......$\mathop A\limits^o $View Solution
- 5નાઈટ્રેશન તરફ સક્રિયતાના (reactivity) ચઢતા ક્રમમાં નીચેનાંને ગોઠવોઃView Solution
$A$. $p$-ઝાયલીન $B$. બ્રોમોબેન્ઝિન $C$. મેસિટિલિન $D$. નાઈટ્રોબેન્ઝિન $E$. બેન્ઝિન
નીચે આપેલા વિકલ્પોમાંથી યોગ્ય ઉત્તર પસંદ કરો.
- 6જ્યારે ${(C{H_3})_3} - C - {(C{H_2})_3} - CH - C{H_3} - C{H_2} - C{H_3}$- સમૂહો બેંઝાઇલ કેView Solution
અસંતૃપ્ત સમૂહ સાથે જોડાયેલા હોય ત્યારે તેમની પ્રેરક અસરની ગોઠવણીનો વધતો ક્રમ શું થશે ?
- 7નીચેના કાર્બોકેટાયનની સ્થાયીતા નો સાચો ક્રમ શું છે ?View Solution
$(i)$ $\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,C{H_3}-CH_2} \\
{\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,|}
\end{array}} \\
{C{H_3} - {C^ + }} \\
{\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,|} \\
{\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,C{H_3}}
\end{array}$$(ii)$ $\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,C{H_3}} \\
{\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,|}
\end{array}} \\
{C{H_3} - {C^ + }} \\
{\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,|} \\
{\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,{H}}
\end{array}$$(iii)$ $\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,C{H_3}} \\
{\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,|}
\end{array}} \\
{C{H_3} - {C^ + }} \\
{\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,|} \\
{\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,C{H_3}}
\end{array}$$(iv)$ $Ph - CH ^{+}-\underline{ CH }_{3}$
- 8$HCOO^-$ એનાયનમાં બે કાર્બન - ઓક્સિજન બંધોએ સમાન લંબાઈમાં જોવા મળે છે તો તેનું કારણ શું હશે ?View Solution
- 9નીચેનામાંથી કયા પરમાણુમાં શૂન્ય સિવાયના દ્વિધ્રુવી ચાકમાત્રા છે?View Solution
$(I)$ $1, 2$ - ડાયબ્રોમોઇથેન ની ગૌચ રચના
$(II)$ $1, 2$ -ડાયબ્રોમોઇથેન ની એન્ટિ રચના
$(III)$ ટ્રાન્સ - $1, 4$ -ડાયબ્રોમોસાયકલોહેકઝેન
$(IV)$ સિસ - $1, 4$ -ડાયબ્રોમોસાયકલોહેકઝેન
$(V)$ ટેટ્રાબ્રોમોઇથેન
$(VI)$ $1, 1$ - ડાયબ્રોમોસાયકલોહેકઝેન
- 10કયો મહત્તમ $pK_a$ ધરાવે છે ?View Solution
