વિધાન: બે પદાર્થો વચ્ચેના ઝડપી સંઘાત એ ધીમાં સંઘાત કરતાં વધારે ઉગ્ર હોય છે: જ્યારે પ્રારંભિક અને અંતિમ વેગ સમાન હોય ત્યારે પણ.
કારણ: પ્રથમ કિસ્સામાં વેગમાન વધારે હોય છે.
AIIMS 2008, Medium
a
In a quick collision, time t is small. As \(F \times t =\) constant, therfore, force involved is large. I.e., collision is more violent in comparison to slow collision . Momentum, \(p = mv\) or \(\therefore p \propto v\) momentum is directly proportional to its velocity, so the momentum is greater in a quicker collision
In a quick collision, time t is small. As \(F \times t =\) constant, therfore, force involved is large. I.e., collision is more violent in comparison to slow collision . Momentum, \(p = mv\) or \(\therefore p \propto v\) momentum is directly proportional to its velocity, so the momentum is greater in a quicker collision
Download our appand get started for free
Experience the future of education. Simply download our apps or reach out to us for more information. Let's shape the future of learning together!No signup needed.*
Similar Questions
- 1View Solutionસંપૂર્ણ અસ્થિતિ સ્થાપક સંઘાતમાં નીચેના પૈકી કયા બે સંઘાતી કણો આવેલા હોય છે.
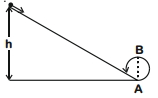
- 2ઘર્ષણરહિત પાટા પર $ h$ ઊંચાઈ એની પ્રારંભમાં સ્થિર રહેલ એક પદાર્થ નીચેની તરફ સરકે છે અને વ્યાસ $AB=D$ ધરાવતું એક અર્ધવર્તુળ પુરૂ કરે છે. આ ઊંચાઈ $h$ કોને બરાબર હશે?View Solution
- 3સ્થિર રહેલ $5 \;\mathrm{m}$ દળનો પદાર્થ ત્રણ ટુકડામાં વિભાજિત થાય છે. બે $m$ દળના પદાર્થ એકબીજાને લંબ રીતે $v$ વેગથી ગતિ કરે છે. તો આ પ્રક્રિયા દરમિયાન કેટલી ઉર્જા ($J$ માં) મુક્ત થઈ હશે?View Solution
- 4$m$ દળવાળું એક આલ્ફા-કણ કોઇ અજ્ઞાત દ્રવ્યમાન ધરાવતા સ્થિર ન્યુક્લિયસ સાથે એક-પારિમાણીય સ્થિતિસ્થાપક અથડામણ અનુભવે છે, અને તેની પ્રારંભિક ગતિઊર્જાનો $64\%$ ગુમાવી ઠીક પાછળની દિશામાં પ્રક્રેરિત થાય છે. તો ન્યુક્લિયસનું દળ કેટલા ................ $\mathrm{m}$ હશે?View Solution
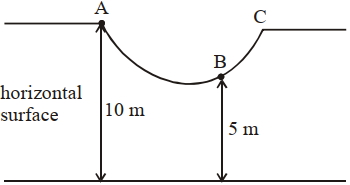
- 5$10$ $kg$નો પદાર્થ $A$ બિંદુથી મુક્તા $B$ બિંદુએ વેગ $x\, m / s$ હોય તો $'x'=........ .$View Solution
- 6$v$ વેગ સાથે ગતિ કરતો $m$ દળનો દડોએ સ્થિર રહેલા બીજા $m$ દળનાં દડા સાથે સન્મુખ અથડામણ અનુભવે છે. જો રેસ્ટિપ્યુશન (સ્થિતિસ્થાપકતા) ગુણાંક $e$ છે અને અથડામણ પછી પહેલા દડાનો વેગ $v_1$ અને બીજા દડાનો વેગ $v_2$ હોય તો $\ldots \ldots \ldots$ હશે ?View Solution
- 7પદાર્થ પર $ \overrightarrow {F\,} = 6\hat i + 2\hat j - 3\hat k $ બળ લાગતાં તેનું સ્થાનાંતર $ \overrightarrow {s\,} = 2\hat i - 3\hat j + x\hat k. $ થાય,જો કાર્ય શૂન્ય હોય,તો $x=$____View Solution
- 8એક મોટર કોઈ પદાર્થને સીધી રેખામાં ગતિ કરવા અચળ બળ પૂરું પાડે છે. તો મોટર દ્વારા ઉદભવેલો પાવર $P$ સમય $t$ સાથે નીચેનામાથી કઈ રીતે બદલાવો જોઈએ ?View Solution
- 9બે સમાન લાદીના ઢેફાઓને બાજુ બાજુએથી બે લાંબી દોરી વડે લટકાવેલા છે. એક બાજુ દોરવામાં આવે છે કે જેથી તેનું ગુરૂત્વકેન્દ્ર $h $ શિરોલંબ અંતર વધે છે. તેને મુક્ત કરવામાં આવે છે અને ત્યારે તે બીજા એક સાથે અસ્થિતિસ્થાપક રીતે સંઘાત પામે છે. તો આ સંયોજનના ગુરૂત્વકેન્દ્રથી વધેલા શિરોલંબ અંતર કેટલું હશે ?View Solution
- 10એક $M = 4\,m$ દળ ધરાવતો ઢાળ(wedge) ઘર્ષણરહિત સમતલ પર છે. $m$ દળ ધરાવતો કણ $v$ વેગથી ઢાળ તરફ ગતિ કરે છે કણ અને સપાટી અને કણ અને ઢાળ વચ્ચેની સપાટી ઘર્ષણરહિત છે તો કણ ઢાળ(wedge) પર મહત્તમ કેટલી ઊંચાઈ સુધી ચડી શકે?View Solution
