What is meant by inflationary gap? State three measures to reduce this gap.
CBSE DELHI - OUTSIDE DELHI - FOREIGN SET 1 2018
The extent at which present aggregate demand is greater than the aggregate demand which is required for full employment level, is known as inflationary gap. This gap is termed as Inflationary Gap because price of goods and services increases in this condition. This condition can be found in economy in the case of Excess Demand. In such cases Aggregate Demand would be more than Aggregate Supply.
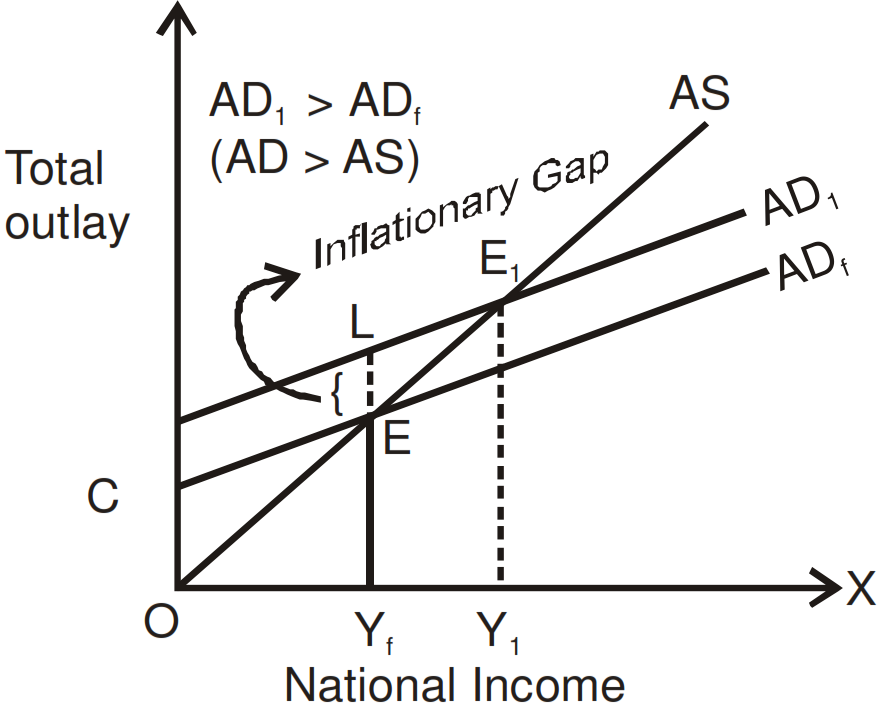
Inflationary Gap $=\ce{ AD_1 - AD_f = LY_f - EY_f = LE}$

Inflationary Gap $=\ce{ AD_1 - AD_f = LY_f - EY_f = LE}$
- Increase in $\text{CRR}:$ Central bank increase the $\text{CRR}$ to control the condition of excess demand, due to this commercial bank has to keep more ratio of its deposits with central bank which decreases their credit creation ability and hence the credit creation also decreases which in turn decreases the money supply and aggregate demand of economy.
- Increase in $\text{SLR}:$ Central bank increases the $\text{SLR}$ to control the condition of excess demand, due to this commercial bank has to keep more ratio of its deposits with itself, which decreases their credit creation ability and hence the credit creatin also decreases which in turn decreases the money supply and aggregate demand also decreases.
- Selling of Securities in Open Market: Central bank starts to sale the securities in open market with the help of commercial banks, this will decreases the availability of cash with commercial banks and hence decreases the credit creation ability of commercial banks. Which would further decreases the credit creation and money supply in an economy and hence aggregate demand also decreases.
Download our appand get started for free
Experience the future of education. Simply download our apps or reach out to us for more information. Let's shape the future of learning together!No signup needed.*
Similar Questions
- 1View SolutionExplain two sources each of demand and supply of foreign exchange.
- 2View SolutionAn economy is in equilibrium. From the following data about an economy calculate autonomous consumption.
- Income = 5000
- Marginal propensity to save = 0.2
- Investment expenditure = 800
- 3Suppose it takes $1.25$ yen to buy a rupee, and the price level in Japan is $3$ and the price level in India is $1.2$. Calculate the real exchange rate between India and Japan $($the price of Japanese goods in terms of Indian goods$). ($Hint: First find out the nominal exchange rate as a price of yen in rupees$).$View Solution
- 4View SolutionThe following figures are based on the balance of payments accounts:
Calculate Balance of Trade.S.No.(₹ in crores)1.Imports of goods.4002.Export of goods.3403.Shipping.34.Travel Tourism, etc.55.Interest, dividends, profits.506.Unilateral Transfers.40 - 5View SolutionExplain the meaning and two merits of fixed foreign exchange rate.
- 6View SolutionWhat is meant by foreign exchange rate? Why does a rise in foreign exchange rate cause a rise in its supply?
- 7View SolutionDefine foreign exchange rate. Why does the demand for foreign exchange rise when its price falls?
- 8View SolutionWould the central bank need to intervene in a managed floating system? Explain why.
- 9View SolutionDistinguish between balance of trade and balance of payment.
- 10View Solution"India is taking huge leaps in the index of Ease of Doing Business, as a result many MNCs are shifting their production base to India." In the light of the above statement, comment upon the flow of foreign exchange and its likely impact on the Indian Economy.
