બે ધાત્વીય તાર $P$ અને $Q$ સમાન કદ ધરાવે છે અને તેઓ સમાન દ્રવ્યનાં બનેલા છે. જો તેમના આડછેદોનો ગુણોત્તર $4: 1$ હોય અને $P$ પર $F_1$ બળ લાગવતાં $\Delta l$ જેટલી લંબઈમાં વધારો થાય છે તો $Q$ માં સમાન વધારો ઉત્પન કરવામાં માટે જરૂરી બળ $F_2 $છે. The value of $\frac{F_1}{F_2}$ is_________થશે.
JEE MAIN 2024, Diffcult
a
\( \mathrm{Y}=\frac{\text { Stress }}{\text { Strain }}=\frac{\mathrm{F} / \mathrm{A}}{\Delta \ell / \ell}=\frac{\mathrm{F} \ell}{\mathrm{A} \Delta \ell} \)
\( \mathrm{Y}=\frac{\text { Stress }}{\text { Strain }}=\frac{\mathrm{F} / \mathrm{A}}{\Delta \ell / \ell}=\frac{\mathrm{F} \ell}{\mathrm{A} \Delta \ell} \)
\( \Delta \ell=\frac{\mathrm{F} \ell}{\mathrm{AY}} \)
\( \mathrm{V}=\mathrm{A} \ell \Rightarrow \ell=\frac{\mathrm{V}}{\mathrm{A}} \)
\( \Delta \ell=\frac{\mathrm{FV}}{\mathrm{A}^2 \mathrm{Y}}\)
\(Y\) & \(V\) is same for both the wires
\( \Delta \ell \propto \frac{\mathrm{F}}{\mathrm{A}^2} \)
\( \frac{\Delta \ell_1}{\Delta \ell_2}=\frac{\mathrm{F}_1}{\mathrm{~A}_1^2} \times \frac{\mathrm{A}_2^2}{\mathrm{~F}_2} \)
\( \Delta \ell_1=\Delta \ell_2 \)
\( \mathrm{~F}_1 \mathrm{~A}_2^2=\mathrm{F}_2 \mathrm{~A}_1^2 \)
\( \frac{\mathrm{F}_1}{\mathrm{~F}_2}=\frac{\mathrm{A}_1^2}{\mathrm{~A}_2^2}=\left(\frac{4}{1}\right)^2=16\)
Download our appand get started for free
Experience the future of education. Simply download our apps or reach out to us for more information. Let's shape the future of learning together!No signup needed.*
Similar Questions
- 1સ્ટીલનો એક તાર $1 \,mm ^2$ આડછેદ અને $1 \,m$ લાંબો છે. આ તારને $200 \,N$ જેટલા બળથી $1 \,mm$ જેટલો ખેંચવામાં આવે છે. તો $10 \,m$ થી $1002 \,cm$ જેટલા ખેચવા માટે ........... $N$ બળની જરૂર પડે.View Solution
- 2સમાન દ્રવ્ય અને સમાન લંબાઇ ધરાવતા તારના વ્યાસનો ગુણોત્તર $1:2$ છે,તેમનાં પર સમાન વજન લગાવતા, લંબાઇમાં થતો વધારાનો ગુણોત્તર કેટલો થાય?View Solution
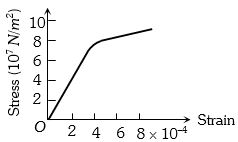
- 3તાર માટે પ્રતિબળ વિરુધ્ધ વિકૃતિનો આલેખ આપેલ છે,તો તારનો યંગ મોડયુલસ $(N/m$${^2}$ મા $)$ કેટલો થાય?View Solution
- 4દ્રવ્યની સામાન્ય ઘનતા $\rho$ અને સ્થિતિસ્થાપકતાનો આયતન માપાંક (bulk modulus of elasticity) $K$ છે. જ્યારે બધીજ બાજુંએથી પદાર્થ પર એક સમાન દબાણ $P$ લાગૂ પાડવામાં આવે ત્યારે દ્રવ્યની ઘનતામાં થતાં વધારાનું મૂલ્ય કેટલું હશે?View Solution
- 5$1\,m{m^2}$ આડછેદ ધરાવતા તારની લંબાઇમાં $1\%$ વધારો કરવા માટે એકમ કદ દીઠ કરવું પડતું કાર્ય કેટલું થાય? $[Y = 9 \times {10^{11}}\,N/{m^2}]$View Solution
- 6કોલમ $-I$ સાથે કોલમ $-II$ નો ચોક્કસ સંબંધ છે, તો તેમને યોગ્ય રીતે જોડો :View Solution
કોલમ $-I$ કોલમ $-II$ $(a)$ તાપમાન વધતા પદાર્થનો યંગ મૉડ્યુલસ $(i)$ શૂન્ય $(b)$ હવા માટેનો યંગ મોડ્યુલસ $(ii)$ અનંત $(iii)$ ઘટે $(iv)$ વધે - 7એક સમઘન પર કદ દબાણ આપવામાં આવે છે અને તેની બધી બાજુમાં $1\%$ નો ઘટાડો થાય થાય તો બલ્ક વિકૃતિ કેટલી થાય ?View Solution
- 8$0.1\, m$ બાજુવાળા સમઘન બ્લોકની ઉપરની બાજુ પર $100\, N$ નું સ્પર્શીયબળ લગાડતાં તે નીચેની બાજુની સાપેક્ષે $0.02\,cm$ ખસે છે,તો સ્પર્શીય વિકૃતિ કેટલી થાય $?$View Solution
- 9સ્ટીલના તારની લંબાઈ $2l$ અને આડછેદ $A \;m ^2$ ધરાવતા આડા તારને બે થાંભલાઓની વચ્ચે રાખવામા આવે છે એન તેની સાથે $m\; kg$ ધરાવતો પદાર્થ જોડવામા આવે છે. અહીં સ્થિતીસ્થાપક સીમા સુધી થતું વિસ્તરણાView Solution
- 10View Solutionસ્થિતિસ્થાપક સ્થિતિઊર્જા ઘનતા માટે નીચેનામાથી શું સાચું છે
