એક લોખંડના ટુકડાને જયોતમાં ગરમ કરવામાં આવે છે. પ્રથમ તે ધુંધળો લાલ બને છે, ત્યારબાદ તે રાતાશ પડતો પીળો બને અને છેલ્લે ગરમ સફેદમાં ફેરવાય છે. ઉપરોકત અવલોકનની સાચી સમજૂતી શેના ઉપયોગથી શકય છે.
AIPMT 2013, Easy
b
According to \(Wien's\) displacement law
According to \(Wien's\) displacement law
\({\lambda _m}T = constant\)
\({\lambda _m} = \frac{{constant}}{T}\)
So when a piece of iron is heated, \({\lambda _m}\) decreases \(i.e.,\) with rise in temperature the maximum intensity of radiation emitted gets shifted towards the shorter wavelengths. So the colour of the heated object will change that of longer wavelength \((red)\) to that of shorter \((reddish\,yellow)\) and when the temperature is sufficiently high and all wavelengths are emitted, the colour will become white.
Download our appand get started for free
Experience the future of education. Simply download our apps or reach out to us for more information. Let's shape the future of learning together!No signup needed.*
Similar Questions
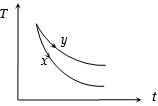
- 1$x$ અને $y$ પદાર્થના તાપમાન $ T \to $ સમય $t$ ના આલેખ આપેલા છે.તેમની ઉત્સર્જકતા અને શોષકતા વચ્ચેનો સબંઘView Solution
- 2અમુક તાપમાને રહેલા પદાર્થમાંથી નીકળતા તરંગની મહત્તમ તરંગલંબાઇ $ 11 \times {10^{ - 5}}cm $ છે,જો પદાર્થનું તાપમાન $ n$ ગણું કરતાં મહત્તમ તરંગલંબાઇ $ 5.5 \times {10^{ - 5}}cm $ થાય છે. તો $n= $_____View Solution
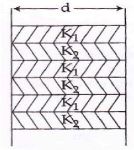
- 3આકૃતિમાં બતાવ્યા પ્રમાણે એક દિવાલમાં એકાંતરે ક્રમશ: $K_1 $ અને $K_2$ ઉષ્મા વાહકતા ધરાવતા $d$ લંબાઇના બ્લોક્સ ધરાવે છે. આ બ્લોક્સના આડછેદના ક્ષેત્રફળ સમાન છે. આ દિવાલની ડાબી અને જમણી બાજુ વચ્ચેની સમતુલ્ય ઉષ્મા વાહકતા કેટલી થાય?View Solution
- 4View Solutionવિધાન : ટ્યુબલાઇટ સફેદ પ્રકાશ ઉત્સર્જિત કરે.
કારણ : ટ્યુબલાઇટમાં પ્રકાશનું ઉત્સર્જન ખૂબ ઊંચા તાપમાને થાય છે.
- 5સ્લેબ સમાન જાડાઈના કોપર અને બ્રાસના બે સમાંતર સ્તર છે અને ઉષ્મીય વાહકતા $1:4$ ના ગુણોત્તર છે. જો બ્રાસની મુક્ત બાજુનું તાપમાન $100°C$ અને કોપરનું $0°C$ છે. તો અત:બાજુનું તાપમાન ....... $^oC$ છે.View Solution
- 6$600\,K$ તાપમાને રહેલ ગોળાને $200\,K$ તાપમાનવાળા વાતાવરણમાં મુકેલ છે.તેનો ઠંડા પડવાનો દર $H$ છે.જો તેનું તાપમાન ઘટીને $400\,K$ થાય તો તેટલા જ વાતાવરણમાં તેનો ઠંડા પડવાનો દર કેટલો થાય?View Solution
- 7કલ્પના કરો કે સૂર્યની બહારની ગોળાકાર સપાટીની ત્રિજયા $r$ છે અને તે $t^oC$ જેટલા તાપમાને સંપૂર્ણ કાળા પદાર્થની માફક ઊર્જાનું ઉત્સર્જન કરે છે, તો સૂર્યના કેન્દ્રથી $R$ જેટલા અંતરે આવેલ એકમ ક્ષેત્રફળવાળી સપાટી (જે આપાતકિરણોને લંબરૂપે છે. ) વડે મેળવાતો પાવર કેટલો હશે?View Solution
જ્યાં $\sigma=$ સ્ટિફનનો અચળાંક છે.
- 8જ્યારે કાળો પદાર્થ ઠંડો પડે તેનું તાપમાન $3000K$ છે. મહત્તમ ઉર્જા ઘનતાને અનુલક્ષીને તરંગલંબાઈમાં $\Delta$$\lambda = 9$ માઈક્રોનનો ફેરફાર થાય છે. હવે કાળા પદાર્થનું - તાપમાન ..... $K$ $(b = 3 ×10^{-3} mk)$View Solution
- 9View Solutionઉષ્માવિકિરણને શોધવા માટેનું સાધન કયું છે?
- 10ગરમ પાણીનું તાપમાન $61^oC$ થી $59^oC$ થતા $10$ minutes લાગે છે,તો પદાર્થનું તાપમાન $51^oC$ થી $49^oC$ થતાં લાગતો સમય ...... $\min$ શોધો.વાતાવરણનું તાપમાન $30^oC$ છે.View Solution
