નીચેના સંયોજન પૈકી આયનીય,સહ-સંયોજક ,સવર્ગ સહ-સંયોજક તેમજ હાઈડ્રોજનબંધ ધરાવેછે?
Diffcult
a
The structure of \(\mathrm{CuSO}_{4} .5 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}\) in the solid-state is shown above. The \(\mathrm{Cu}^{2+}\) ions are attracted towards \(\mathrm{SO}_{4}^{2-}\) ions not only by ionic interactions (electrovalent) but also by coordinate covalent bonds.
The structure of \(\mathrm{CuSO}_{4} .5 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}\) in the solid-state is shown above. The \(\mathrm{Cu}^{2+}\) ions are attracted towards \(\mathrm{SO}_{4}^{2-}\) ions not only by ionic interactions (electrovalent) but also by coordinate covalent bonds.
The \(\mathrm{Cu}^{2+}\) ions form coordinate covalent bonds with water as well as sulfate ions. There are covalent bonds in water and sulfate ions.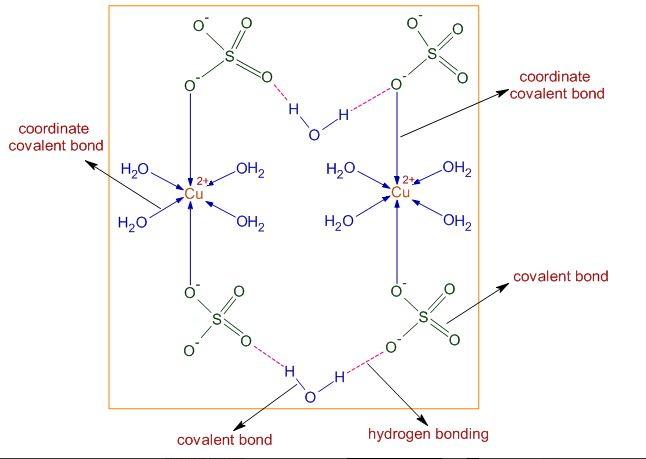
Download our appand get started for free
Experience the future of education. Simply download our apps or reach out to us for more information. Let's shape the future of learning together!No signup needed.*
Similar Questions
- 1$XeF_4$ નું સાચું બંધારણ અને સંકરણ.....View Solution
- 2View Solutionનીચેનામાંથી ક્યા ઘનનું મહત્તમ ગલનબિંદુ છે?
- 3જ્યારે આયનીય સંયોજન $A^+ B^-$ રચાય ત્યારે સંભવિત હોય છેView Solution
- 4View Solutionનીચે આપેલ પ્રક્રમોમાંથી કયામાં બંધક્રમાંક વધે છે અને અનુચુંબકીય પ્રકૃતિમાંથી પ્રતિચુંબકીયમાં ફેરફાર થાય છે ?
- 5ઓઝોનના ઓક્સિજન પરમાણુઓ ઉપર ઈલેકટ્રોનો ના અબંંધકારક યુગ્મોની કુલ સંખ્યા $..........$ છે.View Solution
- 6$IF_7$ નું બંધારણ ............. છે.View Solution
- 7View Solutionધાતુનો ચળકાટ નીચેનામાંથી કોના કારણે હોય છે?
- 8View Solutionનીચેનામાંથી ક્યા ઘટકનું બંધારણ નિયમિત સમચતુષ્ફલકીય છે?
- 9View Solutionબોરોન સહસંયોજક સંયોજન બનાવે છે કારણ કે
- 10View Solutionનીચેનામાંથી ક્યા અણુમાં સૌથી નાનો બંધ ખૂણો છે?
