પાતળો દ્વિ અંતર્ગોળ લેન્સ ઘણા પાતળા પારદર્શક પદાર્થનો બનેલો છે. જો તેમાં હવા અથવા બે પ્રવાહી $L_1$ અને $L_2$ જેનો વક્રીભવનાંક $n_1$ અને $n_2$ ($n_2>n_1>1$) છે તેને ભરી શકાય છે. લેન્સ પ્રકાશના સમાંતર પુંજનું અભિસરણ કરશે જો તે ........થી ભરેલો હોય.
IIT 2000, Medium
d
(d) \(\frac{1}{f} = \left( {\frac{{{n_2}}}{{{n_1}}} - 1} \right)\,\,\left( {\frac{1}{{{R_1}}} - \frac{1}{{{R_2}}}} \right)\)
(d) \(\frac{1}{f} = \left( {\frac{{{n_2}}}{{{n_1}}} - 1} \right)\,\,\left( {\frac{1}{{{R_1}}} - \frac{1}{{{R_2}}}} \right)\)
where \({n_2}\) and \({n_1}\) are the refractive indices of the material of the lens and of the surroundings respectively. For a double concave lens,
\(\left( {\frac{1}{{{R_1}}} - \frac{1}{{{R_2}}}} \right)\) is always negative.
Hence \(f\) is negative only when \({n_2} > {n_1}\)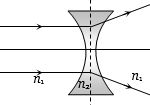
Download our appand get started for free
Experience the future of education. Simply download our apps or reach out to us for more information. Let's shape the future of learning together!No signup needed.*
Similar Questions
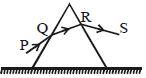
- 1પ્રકાશનું કિરણ પ્રિઝમ પર $60°$ ના કોણે આપાત થાય છે અને પ્રિઝમનો વક્રીભવકોણ $30°$ છે. નિર્ગમન કિરણ આપાત કિરણ સાથે $30°$ નો ખૂણો બનાવે છે. પ્રિઝમના વક્રીભવનાંકની કિંમત ......થશે.View Solution
- 2$f$ કેન્દ્રલંબાઇ ધરાવતા બર્હિગોળ લેન્સને આકૃતિ મુજબ કાપતાં એક ટુકડાની કેન્દ્રલંબાઇ કેટલી થાય?View Solution

- 3અહીં દર્શાવેલ આકૃતિમાં લેન્સના સંયોજનની સમતુલ્ય કેન્દ્રલંબાઈ ($cm$ માં) કેટલી છે? (બધા જ સ્તરો પાતળા ધારો)View Solution
- 4પહેલાં માધ્યમમાં પ્રકાશનો વેગ $v_1$, બીજામાધ્યમમાં વેગ $v_2$ ત્યારે પહેલાં માધ્યમની સાપેક્ષે બીજા માધ્યમનો વક્રીભવનાંક ......થશે.View Solution
- 5View Solutionસમક્ષિતિજ ટેબલ પર મૂકેલા સમબાજુ કાચના પ્રિઝમ પર આપાત થાય છે. ન્યૂનત્તમ વિચલન માટે શું સાચું છે?
- 6આંખનો વિભેદન પાવર $1\, minute$ છે,$3\, metre$ અંતરે રહેલા બે માણસને કેટલા......$km$ અંતર $r$ સુધી અલગ- અલગ જોઇ શકાય?View Solution
- 7બહિર્ગોળ લેન્સ (કેન્દ્રલંબાઈ $20\, cm$) અને અંતર્ગોળ અરીસો એક જ અક્ષ પર એકબીજાથી $80\, cm$ પડેલા છે.અંતર્ગોળ અરીસો બહિર્ગોળ લેન્સની જમણી બાજુએ છે.બહિર્ગોળ લેન્સથી $30\, cm$ અંતરે વસ્તુ મુક્તા તેનું પ્રતિબિંબ, અંતર્ગોળ અરીસો દૂર કરવામાં આવે તો પણ તેજ સ્થાને મળે છે.વસ્તુને અંતર્ગોળ અરિસાથી મહત્તમ કેટલા.......$cm$ અંતરે મુક્તા અરીસા વડે તેનું આભાસી પ્રતિબિંબ મળે?View Solution
- 8સમબાજુ પ્રિઝમનો ક્રાંતિકોણ $45^o $ છે.આપાતકિરણ એકસપાટીને લંબ હોય,તો...View Solution
- 9હવામાં લાલ રંગની તરંગલંબાઈ $760\, nm$ છે. જ્યારે પ્રકાશ $\left(n=\frac{4}{3}\right)$ વક્રીભવનાંકના પાણીમાંથી પસાર થાય છે, ત્યારે તરંગલંબાઈ $570\, nm$ બને છે. (હવામાં પીળા પ્રકાશની તરંગલંબાઈ $570 \,nm$ છે.) તો પાણીમાં લાલ પ્રકાશનો રંગ કેવો છે?View Solution
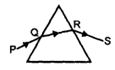
- 10સમતલ સપાટી પર સમબાજુ પ્રિઝમ મૂકેલા છે. $PQ$ કિરણ આપાત કરવામાં આવે છે. તો લઘુતમ વિચલન માટેView Solution