For the reaction,
\(CaCO_{3(g)} \rightleftharpoons CaO_{(s)} + CO_{2(g)}\)
\(K_p = P_{CO_2}\) and \(K_C = [CO_2]\)
\((\because [CaCO_3] = 1\) and \([CaO] = 1\) for solids\()\)
According to Arrhenius equation we have
\(K = A{e^{ - \Delta H{^\circ _r}/RT}}\)
Taking logarithm, we have
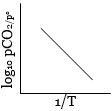
\(\log {K_p} = \log\, A - \frac{{\Delta H_r^o}}{{RT(2.303)}}\)
This is an equation of straight line. When \(log \,K_p\) is plotted against \(1 / T\). we get a straight line.
The intercept of this line = \( log \,A\), slope \(= -\Delta H^°_r / 2.303 \,R\)
Knowing the value of slope from the plot and universal gas constant \(R\), \(∆H^°_r\) can be calculated.
(Equation of straight line : \(Y = mx + C\). Here,
\(\log {K_p} = - \frac{{\Delta H_r^o}}{{2.303R}}\left( {\frac{1}{T}} \right) + \log A\)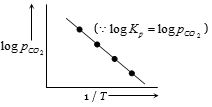
Download our appand get started for free
Similar Questions
- 1$300\,\,K\,\,40\,\,\% HI$ પર વિધટન પામી $H _{2}$ અને $I _{2}$ બનાવે છે. એક વાતાવરણના દબાણે આ વિધટન પ્રક્રિયા માટે $\Delta G ^{\ominus}$ નું મૂલ્ય $\dots\dots\dots\,\,J\,mol ^{-1}$ શોધો. (નજીકના પૂર્ણાંકમાં)View Solution
(ઉપયોગ $R =8.31\, J\, K ^{-1}\, mol ^{-1} ; \log 2=0.3010$. In $10=$ $2.3, \log 3=0.477$ )
- 2પ્રક્રિયા $N_{2(g)} + O_{2(g)} $ $\rightleftharpoons$ $ 2NO_{(g)}$ અને $\frac{1}{2}{N_2} + \frac{1}{2}{O_2}$ $\rightleftharpoons$ $NO$ ના સંતુલન અચળાંક અનુક્રમે $K_1$ અને $K_2$ હોય તો તેમનો સંબંધ.....View Solution
- 3$H_2O_{(l)}$ $\rightleftharpoons$ $ H_2O_{(g)}$ સંતુલન પ્રક્રિયા માટે જો દબાણ વધે તો શું થાય છે ?View Solution
- 4View Solutionનીચેના પૈકી કઇ પ્રક્રિયામાં, પાત્રના કદનો વધારો નીપજોના સર્જનની તરફેણ કરશે ?
- 5પ્રક્રિયા ${A_{(g)}}\, + \,2{B_{(g)}}\, \rightleftharpoons \,\,2{C_{(g)}}$ માટે $2\,L$ કદના પાત્રમાં $A$ ના $1$ મોલ અને $B$ ના $1.5$ મોલ લેવામાં આવે છે. જો સંતુલને $C$ ની સાંદ્રતા $0.35\,M$ હોય, તો પ્રક્રિયાનો સંતુલન અચળાંક $K_c$ .......$M^{-1}$ થશે.View Solution
- 6$5.1\, g\, NH_4SH$ ને $327^oC$ પર એક $3.0\,L$ (નિર્વાતિત)ખાલી કરેલા ફ્લાસ્કમાં નાખવામાં આવે છે. $30\%$ જેટલા ઘન $NH_4SH$ નું $NH_3$ અને $HS$ વાયુ સ્વરૂપે વિઘટન થાય છે. તો $327^oC$ પર પ્રક્રિયાનો $K_p$ કેટલો થશે?View Solution
($R = 0.082\, L\, atm\, mol^{-1}\, K^{-1}$, મોલર દળ $S = 32\, g\, mol^{-1}$, મોલર દળ $N = 14\, g\, mol^{-1}$)
- 7સંતુલન પ્રક્રિયા માટે $\Delta G°= 0$, સંતુલન અચળાંક $k$ = ........View Solution
- 8એક પ્રક્રિયા માટે $\Delta G° = -115$ કિલોજૂલ છે, તો $298 \,K$ તાપમાને $log\, K_p$ = …..View Solution
- 9પ્રક્રિયા ${N_{2(g)}} + {O_{2(g)}}$ $\rightleftharpoons$ $2N{O_{(g)}}$ માટે $T$ તાપમાને સંતુલન અચળાંક $4 \times {10^{ - 4}}$ છે. તો પ્રક્રિયા $N{O_{(g)}}$ $\rightleftharpoons$ $\frac{1}{2}{N_{2(g)}} + \frac{1}{2}{O_{2(g)}}$ માટે આ જ તાપમાને સંતુલન અચળાંક ............. થશે.View Solution
- 10પ્રક્રિયા $N_2$$_{(g)}$ $+$ $O_2$$_{(g)}$ $\rightleftharpoons$ $2NO$$_{(g)}$ માટે સંતુલન અચળાંક $K_1$ છે તથા પ્રક્રિયા $2NO$$_{(g)}$ $+$ $O_2$$_{(g)}$ $\rightleftharpoons$ $2N$$O_2$$_{(g)}$ માટે સંતુલન અચળાંક $K_2$ છે. તો પ્રક્રિયા $N$$O_2$$_{(g)}$ $\rightleftharpoons$$\frac{1}{2}{N_{2(g)}}\, + \,\,{O_{2(g)}}$માટે સંતુલન અચળાંક $K$ ની કિમત......થશે.View Solution