ત્રણ વિદ્યુતભાર $+q$, $-2q$ અને $+q$ અનુક્રમે $(x = 0,\,y = a,\,z = 0)$, $(x = 0,\,y = 0,\,z = 0)$ અને $(x = a,\,y = 0,\,z = 0)$ પર મૂકેલા છે. આ તંત્રની પરિણામી વિદ્યુત ડાઈપોલ સદીશનું મૂલ્ય અને દિશા કેટલા થશે?
AIIMS 2008,AIPMT 2007, Medium
b
The given charge assembly can be represented using the three co-ordinate axes \(\mathrm{x}, \mathrm{y}\) and \(\mathrm{z}\) as shown in figure.
The given charge assembly can be represented using the three co-ordinate axes \(\mathrm{x}, \mathrm{y}\) and \(\mathrm{z}\) as shown in figure.
The charge \(-2 q\) is placed at the origin \(\mathrm{O}\). One \(+q\) charge is place at \((a, 0,0)\) and the other \(+q\) charge is placed at \((0, a, 0) .\) Thus the system has two dipoles along \(x-\)axis and \(y-\)axis respectively.
As the electric dipole moment is directed from the negative to the positive charge hence the resultant dipole moment will be hong \(\overline{\mathrm{OA}}\) where co-ordinates of point \(\mathrm{A}\) are \((a, a, 0) .\) The magnitude of each dipolemoment,
\(p=q a\)
So, the magnitude of resultant dipole moment is
\(\mathrm{P}_{\mathrm{R}}=\sqrt{\mathrm{p}^{2}+\mathrm{p}^{2}}=\sqrt{(\mathrm{qa})^{2}+(\mathrm{qa})^{2}}\)
\(=\sqrt{2}\, \mathrm{qa}\)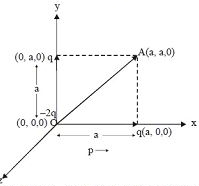
Download our appand get started for free
Experience the future of education. Simply download our apps or reach out to us for more information. Let's shape the future of learning together!No signup needed.*
Similar Questions
- 1$100 \,mg$ ના એક વિદ્યુતભારિત કણને $1 \times 10^{5} \,NC ^{-1}$ જેટલી તીવ્રતા ધરાવતા નિયમિત વિદ્યુતક્ષેત્રની વિરૂદધ દિશામાં ફેકવામાં આવે છે. જે કણ પરનો વિદ્યુતભાર $40 \,\mu C$ અને પ્રારંભિક વેગ $200 \,ms ^{-1}$ હોય તો તે ક્ષણિક વિરામસ્થિતિમાં આવતા પહેલા કેટલું અંતર ($m$ માં) કાપ્શે?View Solution
- 2$+8 \times 10^{-6} \,C$ અને $-8 \times 10^{-6} \,C$ ધરાવતા બે બિંદુવત વીજભારો $A$ અને $B$ ને $d$ અંતરે મૂકવામાં આવ્યા છે. બે વિદ્યુતભારોની વચ્ચે મધ્યબિંદુ $O$ આગળ વિદ્યુતક્ષેત્રની તીવ્રતા $6.4 \times 10^{4}\,NC ^{-1}$ છે. બિંદુવત વિદ્યુતભારો $A$ અને $B$ વચ્ચેનું અંતર $'d'$..........$m$ હશે.View Solution
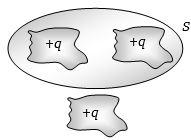
- 3પૃષ્ઠ $S$ માંથી કેટલું વિદ્યુત ફલ્કસ પસાર થાય?View Solution
- 4બે સમાંતર સુવાહક પૃષ્ઠોની એકબાજુનું ક્ષેત્રફળ $A$ છે. જો કોઈ એક પૃષ્ઠને વિદ્યુતભાર $Q$ આપવામાં આવે અને બીજીને તટસ્થ રાખવામાં આવે, તો બંને પૃષ્ઠોની વચ્ચે કોઈ બિંદુ પાસે વિદ્યુતક્ષેત્ર કેટલું છે ?View Solution
- 5જો ડાઇપોલની અક્ષ પર $x$ જેટલા અંતરે વિદ્યુતક્ષેત્રની તિવ્રતા તેની વિષૃવરેખા પર $y$ જેટલા અંતરે વિદ્યુતક્ષેત્રની તિવ્રતા સમાન હોય તો $x:y$ ....View Solution
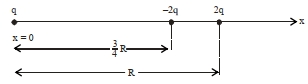
- 6ત્રણ બિંદુવત વીજભારો $q,-2 q$ અને $2 q , x$-અક્ષ પર $x=0, x=\frac{3}{4} R$ અને $x=R$ અંતરે અનુક્રમે ઉદગમથી મૂકેલા આકૃતિમાં દર્શાવેલ છે. જો $q =2 \times 10^{-6}\,C$ અને $R=2\,cm$ હોય તો $-2 q$ વિદ્યુતભારને અનુભવતું પરિણામી બળ ..........$N$ છે.View Solution
- 7બે પાતળી ધાતુની પ્લેટ પર સમાન અને વિરુધ્ધ સંજ્ઞા ધરાવતી વિજભાર ઘનતા $(\sigma = 26.4 \times 10^{-12}\,c/m^2)$ છે.બે પ્લેટ વચ્ચે વિદ્યુતક્ષેત્ર કેટલું હશે?View Solution
- 8ઉગમબિંદુ $O$ આગળ તેના કેન્દ્ર સાથે $X - Y$ સમતલમાં $R$ ત્રિજ્યાની ધન વિદ્યુતભારીત પાતળી ધાતુની રીંગ નિયત કરેલી છે. બિંદુ $(0, 0, Z_0)$ આગળ એક ઋણ વિદ્યુતભારીત કણ $P$ ને સ્થિર સ્થિતિએથી છોડવામાં આવે છે. જ્યાં $(Z_0 > 0)$ તો ગતિ છે.View Solution
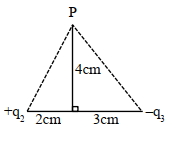
- 9આકૃત્તિમાં દર્શાવ્યા મુજબ, $Y$-અક્ષ પરના $P$ બિંદૂ ઓ પરિણામી વિદ્યુતક્ષેત્ર શૂન્ય હોય તો $\left|\frac{q_2}{q_3}\right|$ નો ગુણોત્તર $\frac{8}{5 \sqrt{x}}$ છે, જ્યાં $x=$. . . . . . .View Solution
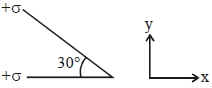
- 10બે $+\sigma$ પૃષ્ઠ વિજભાર ઘનતા ધરાવતા અનંત સમતલને એક બીજા સાથે $30^{\circ} $ ના ખૂણે મૂકવામાં આવે છે, તો તેમની વચ્ચેના ક્ષેત્રમાં વિદ્યુતક્ષેત્ર કેટલું થાય?View Solution