(c) Let us suppose a bar magnet of length \(2l\) is placed inside the magnetic field \((B).\)
Torque\((t)\) \(=\) Force acting \(\times\) perpendicular distance \((d).\)
Force acting \(=B m\)
\(\sin \theta=\frac{d}{2 l}\)
\(T=B m \times d\)
\(d=2 l \sin \theta\)
\(T=B m \cdot 2 l \sin \theta\)
\(M=m \times 2 l T=M B \sin \theta\)
\(T=-\vec{B} \times \vec{M}\)
\(T=\vec{M} \times \vec{B}\)
Where \(; B=\) Magnetic field of induction.
\(M=\) magnetic moment.
\(m=\) pole strength of bar magnet.
\(d=\) perpendicular distance.
\(2 l=\) length of bar magnet.
\(T=\) torque.
Hence, the answer is \(\vec{M} \times \vec{B}\).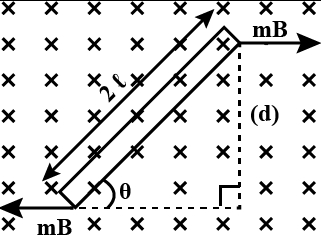
Download our appand get started for free
Similar Questions
- 1$2.5\,m$ વ્યાસ, $400$ આંટા અને $2\,A$ પ્રવાહ ધારીત ટોરોઈડમાં ચુંબકીય ક્ષેત્ર $10 \, T$ હોય તો એકમ લંબાઈ દીઠ બદ્ધ પ્રવાહ ($amp/m$ માં) કેટલો થાય?View Solution
- 2બે ચુંબકના સમાન ધ્રુવો સાથે રાખીને દોલનો કરાવતાં $ 1 $ મિનિટમાં $ 12$ દોલનો થાય છે.હવે,અસમાન ધ્રુવો સાથે રાખીને દોલનો કરાવતાં $ 1$ મિનિટમાં $4$ દોલનો થાય છે.તો ચુંબકોની ચુંબકીય મોમેન્ટનો ગુણોત્તર કેટલો થાય?View Solution
- 3એક ચુંબકનો ઉતર ધ્રુવ ઉતર દિશા તરફ રાખીને મૂકતા, તેના વિષુવવૃત રેખા પર રહેલા $ P$ બિંદુએ ચુંબકીયક્ષેત્ર શૂન્ય થાય છે.હવે ચુંબકને $90˚ $ ફેરવતા $P$ બિંદુએ ચુંબકીયક્ષેત્ર કેટલું થાય? પૃથ્વીના ચુંબકીયક્ષેત્રનો સમક્ષિતિજ ઘટક $B_H$ છે.View Solution
- 4કોઈ એક સ્થાને ડીપ્-એન્ગલ (કોણ) $30^{\circ}$ અને પૃથ્વીનાં ચુંબકીય ક્ષેત્રનો સમક્ષિતિળ ઘટક $0.5$ ઓર્સેટડ છે. પૃથ્વીનું કુલ ચુંબકીય ક્ષેત્ર (ઓર્સેટડમાં) ...................... થશે.View Solution
- 5$0.075 \,kg$ દળ અને $7500 \,kg/m^3 $ ઘનતા ઘરાવતા પદાર્થ ની ચુંબકીય ડાઇપોલ મોમેન્ટ $8 \times 10^{-7} \,Amp \times m^2$ છે.તો મેગ્નેટાઇઝેશન કેટલા .......$Amp/m$ થાય?View Solution
- 6$10 \,A m^2$ ચુંબકીય મોમેન્ટ ધરાવતા બે ગજિયા ચુંબકના કેન્દ્ર વચ્ચેનું અંતર $0.1\, m$ છે.તેમને સમઅક્ષિય મૂકેલાં હોય,તો તેમની વચ્ચે કેટલા.....$N$ બળ લાગે?View Solution
- 7બે સરખાં ગજિયા ચુંબકોને $d$ અંતરે જડેલા છે. આકૃતિમાં દર્શાવ્યા મુજબ સ્થિર વિદ્યુતભાર $Q$ ને બંને ચુંબકોનાં વચ્ચેનાં ભાગમાં $P$ બિંદુએ કેન્દ્ર $O$ થી $D$ અંતરેથી રાખવામાં આવે છે. $Q$ વિદ્યુતભાર પર લાગતું બળView Solution
- 8View Solutionચુંબકીય મેરીડીયનને લંબ સમતલમાં નમન (dip) ચુંબકીય સોય કઇ સ્થિતિમાં રહે?
- 9પૃથ્વીના ચુંબકીયક્ષેત્રનો સમક્ષિતિજ ઘટક એ શિરોલંબ ધટક કરતાં $ \sqrt 3 $ ગણો છે.તો તે સ્થળે ડીપ એન્ગલ કેટલા......$^o$ થાય?View Solution
- 10સમચુંબકત્વ પદાર્થો. . . . . . . .View Solution
$A$. બાહ્ય યુંબકીય ક્ષેત્રની દિશામાં આપમેળે ગોઠવાય છે.
$B$. બાહ્ય ચુંબકીય ક્ષેત્ર તરફ પ્રબળતાથી આકર્ષાય છે.
$C$. તમમની ગ્રહણશીલતા શૂન્ય કરતા સહેજ વધારે હોય છે.
$D$. પ્રબળ ચુંબકીય ક્ષેત્ર થી નબળા ચુંબકીય ક્ષેત્ર તરફ ગતિ કરે છે.
નીચે આપેલા વિકલ્પોમાંથી સૌથી યોગ્ય ઉત્તર પસંદ કરોઃ
