- Define “Trade surplus”. How is it different from “Current account surplus”?
- “Indian Rupee (₹) plunged to all time low of ₹ 74.48 against the US Dollar ($)”. -The Economic Times
CBSE 58-1-3 PAPER SET 2019
- Trade surplus refers to the situation when exports of goods and services exceeds the import of goods and services.
Trade surplus is different from "Current Account Surplus". This is because current account is the account which maintains the records of imports and exports of goods and services as well as the record of unilateral transfers.
Current Account Balance = Balance of Visible Trade + Balance of Invisible Trade + Balance of Unilateral Transfers
- Indian Rupee is depreciating against the US Dollar since it is given that "Indian Rupee (₹) plunged to all time low of ₹ 74.48 against the US Dollar ($)". A high exchange rate makes the imports more expensive. Consequently, a rise in the exchange rate implies a reduction in the demand for imports and vice-versa.
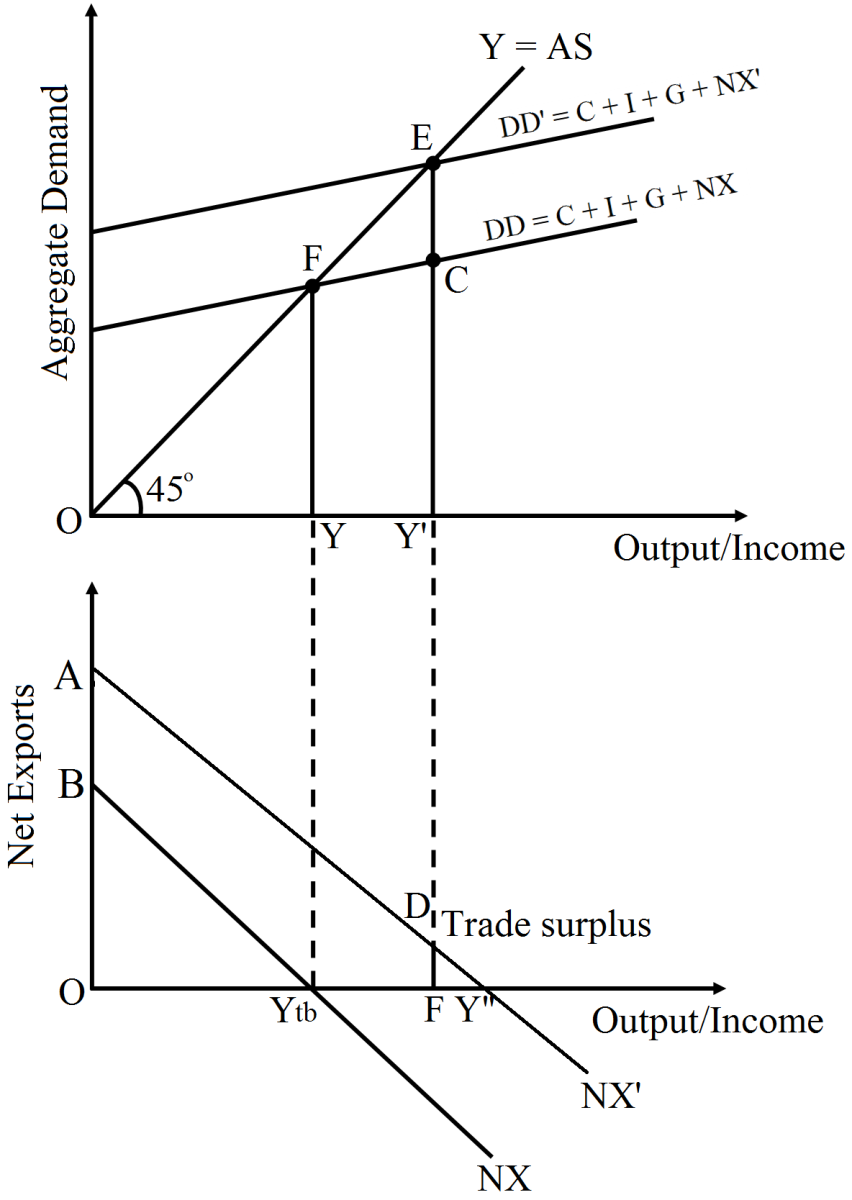
Suppose the initial equilibrium income is given by Ye that corresponds to a trade balance equal to Ytb. With the rise in the net export demand, the aggregate demand curve DD shifts upwards to DD' such that the new equilibrium is established at point E' and the equilibrium income rises to Y'.
In the lower panel due to the fall in the imports, the net export rises and the net export curve shifts upwards from NX to NX'. At the new level of income, the net exports is represented by the vertical distance AE' which are necessarily positive (because the total demand curve DD' lies above the aggregate demand curve AD).
Thus, with a fall in the imports, there is a trade surplus. This trade surplus is represented in the lower panel by the vertical length DF.
Download our appand get started for free
Experience the future of education. Simply download our apps or reach out to us for more information. Let's shape the future of learning together!No signup needed.*
Similar Questions
- 1View SolutionIndian investors borrow from abroad. Answer the following:
- In which sub-account and on which side of the Balance of Payments Account will this borrowing be recorded? Give reason.
- Explain what is the impact of this borrowing on exchange rate.
- 2View SolutionDefine fixed exchange rate. How is the exchange rate determined in a flexible exchange rate system?
- 3View Solution
- In which sub-account and on which side of balance of payments account will foreign investments in India be recorded? Give reasons.
- What will be the effect of foreign investments in India on exchange rate? Explain.
- 4View SolutionGive the meaning of 'foreign exchange' and 'foreign exchange rate'. Giving reason, explain the relation between foreign exchange rate and demand for foreign exchange.
- 5Suppose C = 100 + 0.75Y, $\triangle\text{I}=500,$ G = 750, taxes are 20% of income, X = 150, M = 100 + 0.2Y and classify whether it is budget deficit or surplus and trade deficit or surplus.View Solution
- 6View SolutionIn the above example, if exports change to X = 100, find the change in equilibrium income and the net export balance.
- 7View SolutionThe following figures are based on BoP accounts:
Calculate:S.No.(₹ in crores)1.Import of goods.8002.Export of goods.5503.Import of services (Banking, Shipping, Insurance, Tourism, etc.)504.Export of services (Banking, Shipping, Insurance, Tourism, etc.)1505.Unilateral transfers from rest of the world (Gifts, Aids, etc.)1006.Unilateral transfers to rest of the world (Gifts, Aids, etc.)807.Capital receipts (Loan from foreigners, Sale of assets to foreigners, Receipt of capital from foreigners).2008.Capital Payments (Loans to foreigners, Buying of assets from foreigners, Payment of capital to foreigners).70- Balance of Trade.
- Balance of Payments on Current Account.
- Balance Payments on Capital Account.
- Balance of Payments.
- 8View SolutionSuppose C = 40 + 0.8Y D, T = 50, I = 60, G = 40, X = 90, M = 50 + 0.05Y.
- Find equilibrium income.
- Find the net export balance at equilibrium income.
- What happens to equilibrium income and the net export balance when the government purchases increase from 40 and 50?
- 9View SolutionExplain the distinction between autonomous and accommodating' transactions in balance of payments. Also explain the concept of balance of payments 'deficit' in this context.
- 10View SolutionHow is foreign exchange rate determined in the market?
