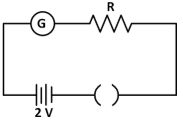
Let full scale deflection of current \(=1\)
In case \(1,\) when \(\mathrm{R}=2400 \Omega\) and deflection of 40 divisions present.
\(\therefore \quad \frac{40}{50} \mathrm{I}=\frac{V}{G+R}\)
\(\Rightarrow \quad \frac{4}{5} \mathrm{I}=\frac{2}{G+2400}\dots (1)\)
In case \(2,\) when \(\mathrm{R}=4900 \Omega\) and deflection of 20 divisions present
\(\therefore \quad \frac{20}{50} \mathrm{I}=\frac{V}{G+R}\)
\(\Rightarrow \quad \frac{2}{5} \mathrm{I}=\frac{2}{G+4900}\dots (2)\)
From \((1)\) and \((2)\) we get,
\(\frac{4}{2}=\frac{G+4900}{G+2400}\)
\(\Rightarrow 2 G+4800=G+4900\)
\(\Rightarrow \mathrm{G}=100 \Omega\)
Putting value of G in equation (1), we get.
\(\frac{4}{5} \mathrm{I}=\frac{2}{100+2400}\)
\(\Rightarrow \mathrm{I}=1 \mathrm{mA}\)
Current sensitivity \(=\frac{\mathrm{I}}{\text { number of divisions }}\)
\(=\frac{1}{50}\)
\(=0.02 \mathrm{mA} /\) division
\(=20 \mu \mathrm{A} /\) division
Resistance required for deflection of 10 divisions
\(\frac{10}{50} \mathrm{I}=\frac{V}{G+R}\)
\(\Rightarrow \frac{1}{5} \times 1 \times 10^{-3}=\frac{2}{100+R}\)
\(\Rightarrow \mathrm{R}=9900 \Omega\)
Download our appand get started for free
Similar Questions
- 1View Solutionસોલેનોઇડમાં ચુંબકીયક્ષેત્રનો છેડાથી અંતરની સાથે થતો ફેરફાર ક્યો ગ્રાફ દર્શાવે છે?
- 2$0.5 \,m $ લંબાઇના સુરેખ વાહક તારમાં $1.2 \,A$ નો વિદ્યુતપ્રવાહ વહે છે. તેને $2\,T$ તીવ્રતાવાળા ચુંબકીય ક્ષેત્રમાં લંબરૂપે મૂકવામાં આવે છે. તાર પર લાગતું બળ ($N$ માં) કેટલું હશે?View Solution
- 3$1\,\mu C$ વિધુતભારિત કણ $(2 \hat{ i }+3 \hat{ j }+4 \hat{ k })\, ms ^{-1} .$ ના વેગથી $(5 \hat{ i }+3 \hat{ j }-6 \hat{ k }) \times 10^{-3}\, T$ ના ચુબકીય ક્ષેત્રમાં ગતિ તેના પર લાગતુ બળ $\overline{ F } \times 10^{-9} N$. હોય તો $\overrightarrow{ F }$View Solution
- 4એક ગેલ્વેનોમીટર પૂર્ણ આવર્તન માટે $10^{-4}\, A$ જેટલો પ્રવાહ માપી શકે છે. તેને $0 -5\, V$ માપી શકે તેવા વોલ્ટમીટરમાં ફેરવવા માટે શ્રેણીમાં $2\, M\,\Omega $ જેટલો અવરોધ જોડાવો પડે છે.તો આ ગેલ્વેનોમીટરને $0-10\, mA$ પ્રવાહ માપી શકે તેવા એમીટરમાં ફેરવવા માટે કેટલા ......$\Omega $ શંટ અવરોધ જોડવો પડે?View Solution
- 5$10\; cm$ બાજુ વાળા એક ચોરસ ગૂંચળાને $20$ આંટા છે અને તેમાંથી $12\; A$ વિદ્યુતપ્રવાહ પસાર થાય છે. આ ગૂંચળુ શિરોલંબ લટકાવેલું છે અને ગૂંચળાના સમતલનો લંબ $0.80 \;T$ મૂલ્યના સમક્ષિતિજ નિયમિત ચુંબકીય ક્ષેત્ર સાથે $30^o$ કોણ બનાવે છે. ગૂંચળું કેટલા મૂલ્યનું ટૉર્ક અનુભવશે?View Solution
- 6View Solutionકોઈ વિસ્તારમાં નિયમિત વિદ્યુતક્ષેત્ર અને નિયમિત ચુંબકીયક્ષેત્ર એક જ દિશામાં છે. જો આ વિસ્તારમાં ઇલેકટ્રોનને અમુક વેગથી ક્ષેત્રની દિશામાં ગતિ કરાવતાં ઇલેકટ્રોન ....
- 7$4.5 \times 10^{5} \;m / s$ના વેગથી ગતિ કરતાં બિંદુવત વિજભારના કારણે ઉત્પન્ન થતાં વિદ્યુતક્ષેત્ર અને ચુંબકીયક્ષેત્રનો ગુણોતર કેટલો થાય?View Solution
- 8શૂન્યાવકાશમાં $0.20 \,m$ અંતરે એમ એકબીજાને સમાંતર રાખેલા બે લાંબા સમાંતર તારોમાંથી $x$ $A$ જેટલો પ્રવાહ સમાન દિશામાં વહે છે. જો દરેક તારનો પ્રતિ મીટર લાગતું આકર્ષણબળ $2 \times 10^{-6} \,N$ હોય તો, $x$ નું મુલ્ય લગભગ.........જેટલું હશે.View Solution
- 9$80\,cm $ લંબાઇ અને $3 \,cm $ ત્રિજયા ધરાવતા સોલેનોઇડમાં $10 \,A$ પ્રવાહ પસાર કરતાં ચુંબકીયક્ષેત્ર $(B = 0.2\,T)$ ઉત્પન્ન થાય છે.તો સોલેનોઇડના તારની લંબાઇ કેટલી થાય?View Solution
- 10તારમાંથી $5\,A$ નો પ્રવાહ પસાર થાય છે,તારથી $0.1\,m$ અંતરે $ 5 \times {10^6}m{s^{ - 1}} $ ના વેગથી ઇલેકટ્રોન તારને સમાંતર ગતિ કરે,તો તેના પર કેટલું બળ લાગતું હશે?View Solution
