એક વાહકતારનો અવરોધ $50^{\circ} C$ તાપમાને $5$ ઓહમ અને $100^{\circ} C$ તાપમાને $6$ ઓહમ છે. તો $0^{\circ} C$ તાપમાને અવરોધ (ઓહમમાં) કેટલો હશે?
AIEEE 2007, Medium
d
We know that
We know that
\(R_{t}=R_{0}(1+\alpha t)\)
where \(R_{t}\) is the resistance of the wire at \(t\,^{o} \mathrm{C}\)
\(R_{0}\) is the resistance of the wire at \(0\,^{o} \mathrm{C}\)
and \(\alpha\) is the temperature coefficient of resistance.
\(\Rightarrow R_{50}=R_{0}(1+50 \alpha)\) ......\((i)\)
\(R_{100}=R_{0}(1+100 \alpha)\) .......\((ii)\)
From \((i),\) \(R_{50}-R_{0}=50 \alpha R_{0}\) .....\((iii)\)
From \((ii),\) \(R_{100}-R_{0}=100 \alpha R_{0}\) ....\((iv)\)
Dividing \((iii)\) by \((iv),\) we get
\(\frac{R_{50}-R_{0}}{R_{100}-R_{0}}=\frac{1}{2}\)
Here, \(R_{50}=5\, \Omega\) and \(R_{100}=6\, \Omega\)
\(\therefore \frac{5-R_{0}}{6-R_{0}}=\frac{1}{2}\)
or, \(6-R_{0}=10-2 R_{0}\) or, \(R_{0}=4\, \Omega\)
Download our appand get started for free
Experience the future of education. Simply download our apps or reach out to us for more information. Let's shape the future of learning together!No signup needed.*
Similar Questions
- 1$200\,\Omega $ ના અવરોધનો એક કલર કોડ છે જેમાં જો લાલ કલરને બદલે લીલો કલર કોડ વાપરવામાં આવે તો નવો અવરોધ કેટલા ................. $\Omega$ થાય?View Solution
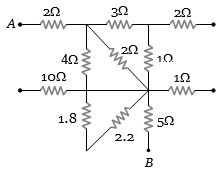
- 2આપેલ પરિપથમાં $A$ અને $B$ વચ્ચેનો સમતુલ્ય અવરોધ કેટલા .................. $\Omega$ થાય?View Solution
- 3એક સમાંતર જોડાણ કે જે સમાન લંબાઈના, સમાન આડછેદનું ક્ષેત્રફળ ધરાવતા અને સમાન દ્રવ્યના ચાર તારોનું બનેલું છે. તેની અસરકારક અવરોધ $0.25\, \Omega$ છે. જો તેઓને શ્રેણીમાં જોડવામાં આવે તો તેમનો અસરકારક અવરોધ કેટલો થશે ? ($\Omega$ માં)View Solution
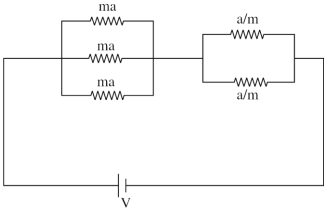
- 4જો આપેલ પરિપથમાં $'a'$ અને $m$ બે યાદચ્છિક અચળાંકો હોય તો પરિપથમાં અવરોધ લધુત્તમ થાય ત્યારે $m$ નું મૂલ્ય $\sqrt{\frac{x}{2}}$ મળે છે. $x$ .............. થશે.View Solution
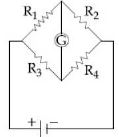
- 5આકૃતિમાંનો વ્હીસ્ટોન બ્રીજ ત્યારે સંતુલિત થાય છે કે જ્યારે ઉપયોગમાં લેવાયેલ કાર્બન અવરોધ $R_1$ ના વર્ણ સંકેત (નારંગી, લાલ, કથ્થઈ) છે. અવરોધો $R_2$ અને $R_4$ અનુક્રમે $80\,\Omega$ અને $40\,\Omega$ છે. આ વર્ણ સંકેત કાર્બન અવરોધોનો સચોટ મૂલ્ય આપે છે એમ ધારતા, $R_3$ તરીકે વાપરેલ કાર્બન અવરોધનો વર્ણ સંકેત ________ હશેView Solution
- 6એક ટેકનિશિયન એ ફક્ત બે અવરોધ ગુંચળા ધરાવે છે. એક પછી એક તેમનો ઉપયોગ, શ્રેણી કે સમાંતર જોડાણમાં કરીને, તે $3,4,12$ અને $16$ ઓહમના અવરોધ મેળવી શકે છે.તો બંને ગૂંચળાનો અવરોધ કેટલો છે.View Solution
- 7દરેકનું $emf$ $E$ અને આંતરિક અવરોધ $r$ ધરાવતાં પાંચ કોષોને શ્રેણીમાં જોડવામાં આવે છે. નજરયૂકના કારણે એક કોષને ખોટી રીતે જોડી દેવામાં આવે છે.તો સંયોજનનો સમતુલ્ય આંતરિક અવરોધ $........r$ છે.View Solution
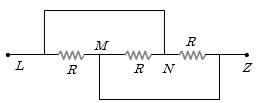
- 8આકૃતિમાં દર્શાવ્યા પ્રમાણે દરેક $R$ મૂલ્યના ત્રણ સમાન અવરોધ જોડેલા છે. $M$ અને $N$ વચ્ચેનો સમતુલ્ય અવરોધ કેટલો થાય?View Solution
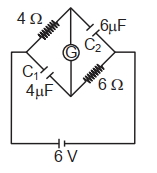
- 9પરિપથમાં આપેલ ગેલ્વેનોમીટર $(G)$ નો અવરોધ $2 \Omega$ હોય તો પરિપથમાં આપેલ $C_1$ અને $C_2$ પરનો વિદ્યુતભારનો ગુણોતર કેટલો થાય.View Solution
- 10તારમાંથી પસાર થતો પ્રવાહ $I$ અને વોલ્ટેજ $V$ છે.તો $\log\,I$ અને $\log\,V$ નો આલેખ કેવો થાય?View Solution
