પાત્રમાં ગેસના $n$ અણુ છે,હવે અણુ $2n$ કરતાં દબાણ કેટલુ થાય?
Easy
c
we know that from ideal gas equation, \(PV = nRT\) now, \(n=\) number of moles of gas \(=\frac{N}{N_{A}}\), where \(N=\) number of molecules of the gas and \(N _{ A }\) is the Avogadro's number
we know that from ideal gas equation, \(PV = nRT\) now, \(n=\) number of moles of gas \(=\frac{N}{N_{A}}\), where \(N=\) number of molecules of the gas and \(N _{ A }\) is the Avogadro's number
So, putting the value of \(n\) in ideal gas equation, we get \(PV =\frac{ N }{ N _{ A }} RT\)
this means that pressure of the gas is proportional to the number of molecules of the gas at constant temperature and volume
So, if we double the number of molecules of the gas \((2 x )\), then pressure will also double
Download our appand get started for free
Experience the future of education. Simply download our apps or reach out to us for more information. Let's shape the future of learning together!No signup needed.*
Similar Questions
- 1View Solutionઅચળ તાપમાને પરમાણુઓ વચ્ચેનું અંતર બમણું કરવામાં આવે તો દબાણ .......થશે.
- 2$27^oC$ તાપમાને અને $30$ વાતાવરણ દબાણે ભરેલા વાયુનું વિસ્તરણ કરીને દબાણ $1$ વાતાવરણ કરવામાં આવે છે,જો કદ $10$ ગણું થાય,તો નવું તાપમાન કેટલું ....... $^oC$ થાય?View Solution
- 3$27°C$ તાપમાને વાયુનું કદ $V$ છે,અચળ દબાણે કદ $1.5\, V$ કરતાં નવું તાપમાન ....... $^oC$ થાય?View Solution
- 4$T$ તાપમાન માટે એક પરમાણ્વિક વાયુ માટે $\bar v , \bar v_{rms}$ અને $v_p$ અનુક્રમે સરેરાશ ઝડપ, $rms$ ઝડપ અને મહત્તમ શક્ય ઝડપ છે. અણુનું દળ $m$ હોય તો .....View Solution
- 5સમોષ્મી પ્રક્રિયા દરમિયાન, વાયુનું દબાણ તેના નિરપેક્ષ તાપમાનના ધનના સમપ્રમાણમાં મળે છે. વાયુ માટે $\frac{\mathrm{Cp}}{\mathrm{Cv}}$ ગુણોત્તર______છે.View Solution
- 6$27°C$ તાપમાને ઓક્સિજનની $rms$ વેગ .... $ms^{-1}$ હશે.View Solution
- 7View Solutionસમાન મોલ ધરાવતા ચાર વાયુના આલેખ આપેલા છે,તો
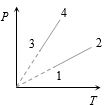
- 8બે સમાનગોળામા $NTP$ એ વાયુ ભરેલ છે. એક ગોળાને બરફમાં અને બીજાગોળાને ગરમપાણીમાં રાખવામાં આવે તો દબાણ $1.5$ ગણુ થાય છે.તો ગરમ પાણીનું તાપમાન ....... $^oC$ હશે?View Solution
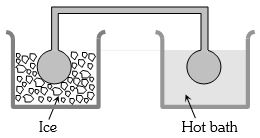
- 9વાયુના $7$ અણુઓની ઝડપ $(6, 4, 2, 0, -2, -4, -6)\, m/s$ હોય,તો $rms$ ઝડપ ....... $m/s$ થાય.View Solution
- 10એક આદર્શ વાયુ માટે અચળ દબાણે મોલર વિશિષ્ટ ઉષ્મા $(7/2) R$ છે. અચળ દબાણે વિશિષ્ટ ઉષ્મા અને અચળ કદે વિશિષ્ટ ઉષ્માનો ગુણોત્તર કેટલો થાય?View Solution
