\({\lambda \propto V}\)
The average time between the collisions of the gas molecules is nothing but the mean free path divided by the root mean square speed of the gas molecules.
\(\mathrm{So}\)
\(\Longrightarrow\left[\text { Time }=t=\frac{\lambda}{v_{R M S}}\right]\)
Now we also know that :-
\(v_{R M S} \propto \sqrt{P V}\)
Using the above we get :-
\(\Longrightarrow t \propto V \times \sqrt{\frac{1}{P V}}\)
\(\Longrightarrow t \propto \sqrt{\frac{V^{2}}{P V}}\)
\(\Longrightarrow t \propto \sqrt{\frac{V}{P}}\)
adiabatic process then \(PV^{\gamma}=constant\)
then \(t \propto V^{\frac{\gamma+1}{2}}\)
Download our appand get started for free
Similar Questions
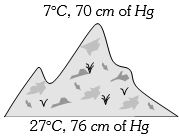
- 1View Solutionઆપેલ આકૃતિ માં પહાડની ટોચ ઉપર અને નીચે ઘનતાનો ગુણોતર કેટલો થાય?
- 2$(1)$ જ્યારે તાપમાન ઘટાડતા વાયુ અણુની સરેરાશ ગતિઊર્જા ઘટે છે.View Solution
$(2)$ દબાણ વધારતા વાયુ આણુની સરેરાશ ગતિઊર્જા વધે છે.
$(3)$ કદ વધારતા વાયુ અણુની સરેરાશ ગતિઊર્જા ઘટે છે.
$(4)$ તાપમાન વધારતા વાયુનું દબાણ વધે છે.
$(5)$ તાપમાન વધારતા વાયુનું કદ ઘટે છે.
નીચે આપેલા વિકલ્પોમાંથી સાચો ઉત્તર પસંદ કરો :
- 3View Solutionએક પરમાણ્વીય વાયુની એક ગ્રામ પરમાણુઓ માટેની સરેરાશ ગતિઊર્જા શોધો.
- 4સામાન્ય તાપમાને અને દબાણે એક ગ્રામ મોલ વાયુની ગતિઊર્જા કેટલી થાય ?($R = 8.31 J/mol - K$)View Solution
- 5View Solutionએક પરમાણ્યિ વાયુ માટે મુકતાતાના અંશો કેટલો હોય?
- 6View Solutionપાત્રની દિવાલ પર વાયુ દબાણ લગાડે છે કારણ કે પરમાણુઓ .......
- 7View Solutionવિધાન : વાયુ માટે સરેરાશ મુક્તપથ ઘનતાના વ્યસ્ત પ્રમાણમા હોય છે
કારણ : વાયુ માટે સરેરાશ મુક્તપથ દબાણના વ્યસ્ત પ્રમાણમા હોય છે
- 8એક મોલ આદર્શ વાયુ પ્રક્રિયા માટે $P\, = {P_0}\,\left[ {1 - \frac{1}{2}{{\left( {\frac{{{V_0}}}{V}} \right)}^2}} \right]$ સમીકરણ પર આધાર રાખે છે.જ્યાં $P_0$ અને $V_0$ અચળાંક છે તો વાયુનું કદ $V_0$ થી $2V_0$ કરતા તાપમાનમા કેટલો ફેરફાર થાય?View Solution
- 9$7\, gm N _{2}$ અને $20\, gm$ $Ar$ નું મિશ્રણ કરતા મિશ્રણનો $C _{ p } / C _{ v }$ કેટલો થાય?View Solution
- 10અચળ કદે આર્ગોનની વિશિષ્ટ ઉષ્મા $0.075 kcal / kg K$ છે. તો પરમાણુભારનું મૂલ્ય.....થાય. [$R = 2 cal/mol K$]View Solution
