$(B)$ ડ્રીફટ-વેગ આપેલ સુવાહકના આડછેદના વ્યસ્ત પ્રમાણમાં હોય છે.
$(C)$ ડ્રિફટ-વેગ એ સુવાહકને લગાવેલ સ્થિતિમાન તફવત ઉપર આધાર રાખતો નથી.
$(D)$ ઈલેક્ટ્રોનનો ડ્રિફટ-વેગ સુવાહકની લંબાઇ પર આધાર રાખલો નથી.
$(E)$ ડ્રિફટ-વેગ સુવાહકનું તાપમાન વધારતા વધે છે.
નીચે આપેલા વિકલ્પોમાંથી સાચો વિકલ્પ પસંદ કરો.
Drift velocity \(=\left(\frac{ e \tau}{ m }\right) E\)
\(v _{ d }=\left(\frac{ e \tau}{ m }\right)\left(\frac{\Delta V }{\ell}\right)\)
\(\Delta V=\) Potential difference applied across the wire
As temperature increases, relaxation time decreases, hence \(V _{ d }\) decreases.
As per formula, \(V _{ d } \propto \frac{1}{\ell}\)
\(v _{ d }=\frac{ I }{\text { neA }}\), as it is not mentioned that current is at steady state neither it is mentioned that \(n\) is constant for given conductor. So it can't be said that \(v _{ d }\) is inversely proportional to \(A\).
\(I=n e A v_{d}=\frac{V}{R}=\frac{V}{\rho \ell} A\)
\(v _{ d }=\frac{ V }{\rho \ell \text { ne }} \quad\left( E =\frac{ V }{\ell}\right)\)
\(v _{ d }=\frac{ eE \tau}{ m }\)
\(\tau\) decrease with temperature increase.
First and fourth statements are correct.
Download our appand get started for free
Similar Questions
- 1આકૃતિમાં દર્શાવેલ પરિપથમાં બધા જ કોષો આદર્શ છે. $2\; \Omega$ અવરોધમાંથી પસાર થતો વિદ્યુતપ્રવાહ $............A$ છે.View Solution
- 2View Solutionઅનિયમિત આડછેદવાળા ધાતુના વાહકને વિદ્યુતસ્થિતિમાનનો તફાવત લાગુ પાડેલ છે. વાહક માટે નીચેનામાંથી કઇ રાશિ અચળ રહે છે?
- 3બે વાહક તારોને શ્રેણીમાં જોડતાં સમતુલ્ય અવરોધ $14\, \Omega$ અને તેમને સમાંતરમાં જોડતાં સમતુલ્ય અવરોધ $3.43\, \Omega$ થાય છે. તો તે પૈકી વધુ મૂલ્ય ધરાવતાં તારનો અવરોધ ................. $\Omega$View Solution
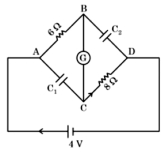
- 4આકૃતિમાં, ગેલ્વેનોમીટર નાં ગૂંચળાનો અવરોધ $G =2\, \Omega$ છે. કોષનું $emf \;4\,V$ છે. $C _1$ અને $C _2$ ની વચ્યેનો વીજસ્થિતિમાનનો તફાવત ......... છે.View Solution
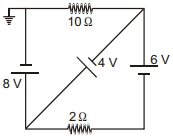
- 5ઓરડામાં સપ્લાય વોલ્ટેજ $120$ $V$ છે.લેડ વાયરનો અવરોધ $6$ $Ω$ છે.ઓરડામાં $60$ $W$ નો બલ્બ પહેલેથી ચાલુ છે.હવે,બલ્બને સમાંતર $240$ $W$ નું હીટર ચાલુ કરવામાં આવે,તો બલ્બને સમાંતર વોલ્ટેજમાં કેટલા ............. $V$ ઘટાડો થશે?View Solution
- 6$r=4.0 \,mm$ ત્રિજ્યાના એક નળાકારીય તારમાં પ્રવાહ ધનતા $1.0 \times 10^{6} \,A / m ^{2}$ છે અને તે તારના આડછેદ પર નિયમિત છે. તારના બહારના ભાગમાં ત્રિજ્યાવર્તી અંતરો $\frac{r}{2}$ અને $r$ ની વચ્ચે પ્રવાહ $x \pi$ $A$ છે. $x$ નું મૂલ્ચ ......... હશે.View Solution
- 7એક પોટેન્શિયોમીટર તારની લંબાઇ $100 \,cm$ છે તથા તેના બે છેડા વચ્ચે ચોકકસ સ્થિતિમાનનો તફાવત લાગુ પાડેલ છે. બે કોષોને શ્રેણીમાં એવી રીતે જોડવામાં આવે જે પહેલા એકબીજાને મદદ કરે તેમ અને પછી વિરુધ્ધ દિશામાં જોડવામાં આવે છે. બંને કિસ્સામાં તટસ્થ બિંદુ તારના ધન છેડેથી અનુક્રમે $50\,cm$ અને $ 10\,cm $ અંતરે મળે છે. $emf$ નો ગુણોત્તર કેટલો મળે?View Solution
- 8આપેલ પરિપથમાં બધા અવરોધ $2\;\Omega$ ના છે. $A$ અને $B$ બિંદુ વચ્ચેનો સમતુલ્ય અવરોધ ($\Omega$ માં) કેટલો થાય?View Solution
- 9View Solutionહીટરમાં વપરાતા ગૂચાળાને બે સમાન ભાગમાં વિભાજિત કરવામાં આવે છે. હવે આમાંથી એક જ ભાગનો ઉપયોગ હીટરમાં થાય છે તો તેમાંથી ઉત્પન્ન થતી ઉષ્મા પહેલા કરતાં કેવી થાય?
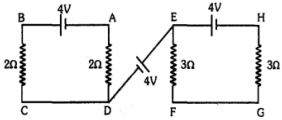
- 10ત્રણ સમાન બેટરીનું $emf\ 4\ V$ અને અવગણ્ય આંતરીક અવરોધ શૂન્ય છે. જેમનું જોડાણ આકૃતિમાં બતાવ્યું છે. બિંદુઓ $A$ અને $G\ (V_A - V_G)$ વચ્ચેનો સ્થિતિમાનનો તફાવત ................ $V$ છે.View Solution