The wavelength of a spectral line in the Lyman series is
\(\frac{1}{\lambda_{L}}=R\left(\frac{1}{1^{2}}-\frac{1}{n^{2}}\right), n=2,3,4, \ldots \ldots\)
and that in the Balmer series is
\(\frac{1}{\lambda_{B}}=R\left(\frac{1}{2^{2}}-\frac{1}{n^{2}}\right), n=3,4,5, \ldots \ldots\)
For the longest wavelength in the Lyman series,
\(n=2\)
\(\therefore \quad \frac{1}{\lambda_{L}}=R\left(\frac{1}{1^{2}}-\frac{1}{2^{2}}\right)=R\left(\frac{1}{1}-\frac{1}{4}\right)=R\left(\frac{4-1}{4}\right)=\frac{3 R}{4}\)
or \(\quad \lambda_{L}=\frac{4}{3 R}\)
For the longest wavelength in the Balmer series,
\(n=3\)
\(\therefore \quad \frac{1}{\lambda_{B}}=R\left(\frac{1}{2^{2}}-\frac{1}{3^{2}}\right)=R\left(\frac{1}{4}-\frac{1}{9}\right)=R\left(\frac{9-4}{36}\right)=\frac{5 R}{36}\)
or \(\quad \lambda_{B}=\frac{36}{5 R}\)
Thus, \(\frac{\lambda_{L}}{\lambda_{B}}=\frac{\frac{4}{3 R}}{\frac{36}{5 R}}=\frac{4}{3 R} \times \frac{5 R}{36}=\frac{5}{27}\)
Download our appand get started for free
Similar Questions
- 1View Solutionઅંધારા ઓરડામાં એક પદાર્થ પર ક્ષ કિરણો આપાત થાય છે તેઓ ........દેખાશે.
- 2$X-ray$ ટયુબના લક્ષય પર $\lambda$ દ-બ્રોગ્લી તરંગલંબાઇ તથા $m$ દ્રવ્યમાનનો ઇલેકટ્રોન અથડાય છે, ત્યારે ઉત્સર્જાતા $X-ray$ ની કટ્-ઓફ તરંગલંબાઇ $ (\lambda_0)$ કેટલી હશે?View Solution
- 3હાઇડ્રોજન પરમાણુની ધરા સ્થિતિની ઊર્જા $ 13.6\, e V$ છે, તો હાઇડ્રોજન પરમાણુની બીજી ઉત્તેજિત અવસ્થામાંથી આયનીકરણ કરવા માટે કેટલી ઊર્જા ($eV$ માં) જરૂરી છે?View Solution
- 4રુથરફોર્ડના પ્રકીર્ણનના પ્રયોગમાં $m_1$ દળ અને $Z_1$ વિદ્યુતભાર ધરાવતો કણ $m_2$ દળ અને $Z_2$ વિદ્યુતભાર ધરાવતા લક્ષ્ય ન્યુકિલયસ પર આપાત કતાં ન્યુકિલયસની નજીક $r_0 $ સુધી જઇ શકે છે, તો કણની ઊર્જાView Solution
- 5હાઇડ્રોજન સ્પેકટ્રમના ઊર્જા સ્તરો આપેલા છે, $A,B$ અને $C$ કઇ શ્રેણી દર્શાવે છે.View Solution
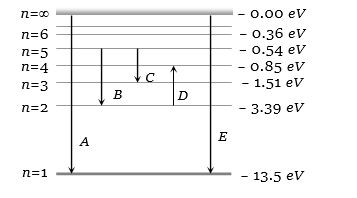
- 6બોહરના મોડલમાં ઇલેક્ટ્રોન પ્રોટોનની ફરતે વર્તુળાકાર કક્ષામાં ભ્રમણ કરે છે. ઇલેક્ટ્રોનની ભ્રમણ કક્ષાને પ્રવાહધારીત વર્તુળાકાર લૂપ લેતા હાઇડ્રોજન પરમાણુમાં જ્યારે ઇલેક્ટ્રોન $n$ મી કક્ષામાં હોય ત્યારે હાઇડ્રોજન પરમાણુની ચુંબકીય મોમેન્ટ કેટલી થાય?View Solution
- 7$Li^{++} $ આયનની આયનીકરણ ઊર્જા ....... છે.View Solution
- 8હાઈડ્રોજન પરમાણુ તેની ધરાસ્થિતિમાં $10.2 \,eV$ ઊર્જાનું શોષણ કરે છે. ઈલેકટ્રોનનું કોણીય વેગમાનનું મૂલ્ય ............... $\times 10^{-34} \; J{s}$ જેટલું વઘશે. (પ્લાન્ક અચળાંક $=6.6 \times 10^{-34} \,Js$ આપેલ છે.)View Solution
- 9હાઈડ્રોજન પરમાણુ માટે બ્રેકેટ શ્રેણીની મહત્તમ તરંગલંબાઈ.........$\mathop A\limits^o $ શોધો.View Solution
- 10View Solutionપારરક્ત વિસ્તારમાં હાઈડ્રોજન પરમાણુની કઈ શ્રેણી આવેલી છે ?
