$l$ લંબાઈના એક ધાતુના તારના બે છેડા વચ્ચેનો સ્થિતિમાનનો તફાવત $V$ મળે છે. જો......હોય તો ડ્રીફટ વેગ બમણો હશે.
Easy
a
The drift velocity is \(v _{ d }=\frac{ eVt }{2 ml }\)
The drift velocity is \(v _{ d }=\frac{ eVt }{2 ml }\)
The relaxation time t changes with change of temperature. Actually it decreases with rise of temperature. Thus at a given temperature drift velocity is directly proportional to the potential difference, inversely proportional to length and is independent of cross-sectional area. So when drift velocity is doubled, \(V\) becomes double and \(l\) is half.
Download our appand get started for free
Experience the future of education. Simply download our apps or reach out to us for more information. Let's shape the future of learning together!No signup needed.*
Similar Questions
- 1$V_0$ વોલ્ટેજ એક વિધુત બલ્બ (ગોળો), $P_0$ પાવર આપે છે. જો વોલ્ટેજ $V$ હોય તો તે …$P$ પાવર આપે છે.View Solution
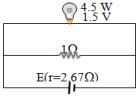
- 2$4.5\, W$, $1.5\, V$ રેટીંગ ધરાવતા બલ્બને આકૃતિમાં દર્શાવ્યા મુજબ લગાડેલ છે. બલ્બને પૂર્ણ પ્રકાશિત કરવા માટે કોષનો $e.m.f$ ................ $V$ હોવો જોઈએ.View Solution
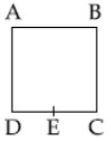
- 3$R$ અવરોધ તારને આકૃતિમાં દર્શાવ્યા પ્રમાણે વાળીને એક $ABCD$ ચોરસ બનાવેલ છે.બિંદુ $E$ અને $C$ વચ્ચેનો સમતુલ્ય અવરોધ કેટલો થાય? ($E$ એ $CD$ નું મધ્યબિંદુ છે)View Solution
- 4ઓપન સર્કિટ સ્થિતિમાં એક વિદ્યુતકોધના બે ધ્રુવોં વચ્યેનો સ્થિતિમાનનો તફાવત $2.2\; V$ છે. તેની સાથે $R = 5\,\Omega $ નો અવરોધ જોડતા આ સ્થિતિમાનનો તફાવત $1.8 \;V$ બને છે. તો આ કોષનો આંતરિક અવરોધ $(r)$ ....... $\Omega$ હશે?View Solution
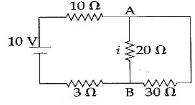
- 5આકૃતિમાં દર્શાવેલ વિદ્યુત પરિપથમાં $AB$ બાજુમાંથી વહેતો પ્રવાહ $i $ કેટલો હશે?View Solution
- 6$0.5\,\Omega$ આંતરિક અવરોધ અને $2\,V$ $e.m.f$ ધરાવતી દરેક છ કોષો વાળી બેટરીને $10\,\Omega$ ના બાહ્ય અવરોધનો ઉપયોગ કરી $220\,V$ $e.m.f$ ના $D.C.$ મેઈન્સ વડે ચાર્જ કરવામાં આવે છે તો ચાર્જિગ વિધુતપ્રવાહ કેટલા ................... $A$ હશે?View Solution
- 7એમિટર અને વોલ્ટમીટર શ્રેણીમાં (કોષ) સાથે જોડેલાં છે. તેઓના અવલોકનો અનુક્રમે $A$ અને $V$ છે. જો હવે અવરોધને વોલ્ટ મીટર સાથે સમાંતરમાં જોડવામાં આવે તો...View Solution
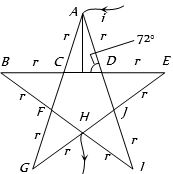
- 8નીચેના સ્ટાર પરીપથમાં $A$ અને $H$ વચ્ચેનો સમતુલ્ય અવરોધ.....View Solution
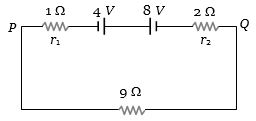
- 9$4\,V$ અને $8 \,V$ $e.m.f.$ ધરાવતી બે બેટરીના આંતરિક અવરોધ અનુક્રમે $1\, \Omega$ અને $2\,\Omega$ છે. તેને $9 \,\Omega$ અવરોધ સાથે આકૃતિમાં દર્શાવ્યા પ્રમાણે જોડેલ છે. તો પરિપથમાં $P$ અને $Q$ માંથી પસાર થતો પ્રવાહ અને તેમની વચ્ચેનો વિદ્યુતસ્થિતિમાનનો તફાવત કેટલો હશે?View Solution
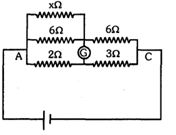
- 10ગેલ્વેનોમીટર આવર્તન (વિચલન) બતાવતું નથી. રીએક્ટન્સ $x$ ....................... $\Omega$ છે ?View Solution