Energy in joule \((E)\)
\(=\) charge \(\times\) potential diff. in volt
\({{\text{E}}_{{\text{electron }}}} = {q_{\text{e}}}{\text{V}}\) and \({{\text{E}}_{{\text{proton }}}} = {q_{\text{p}}}4{\text{V}}\)
de-Broglie wavelength
\(\lambda=\frac{\mathrm{h}}{\mathrm{P}}=\frac{\mathrm{h}}{\sqrt{2 \mathrm{mE}}}\)
\(\lambda_{\mathrm{c}}=\frac{\mathrm{h}}{\sqrt{2 \mathrm{m}_{\mathrm{e}} \mathrm{e} \mathrm{V}}}\) and \(\lambda_{\mathrm{P}}=\frac{\mathrm{h}}{\sqrt{2 \mathrm{m}_{\mathrm{p}} \mathrm{e} 4 \mathrm{V}}}\)
\({\text{(}}\because {q_c} = {q_p}{\text{)}}\)
\(\therefore \frac{{{\lambda _{\text{c}}}}}{{{\lambda _{\text{P}}}}} = \frac{{\frac{{\text{h}}}{{\sqrt {2{{\text{m}}_{\text{e}}}{\text{eV}}} }}}}{{\frac{{\text{h}}}{{\sqrt {2{{\text{m}}_p}{\text{e4V}}} }}}}\) \( = \sqrt {\frac{{2{{\text{m}}_p}{\text{e4V}}}}{{2{{\text{m}}_e}{\text{eV}}}}} \)
\( = 2\sqrt {\frac{{{{\text{m}}_{\text{p}}}}}{{{{\text{m}}_{\text{e}}}}}} \)
Download our appand get started for free
Similar Questions
- 1ઇલેક્ટ્રોન , આયોનાઈઝ હિલિયમ $\left( He ^{++}\right)$ અને પ્રોટોન પાસે સમાન ગતિ-ઉર્જા છે, તેમની દ-બ્રોગ્લી તરંગલંબાઈ $\lambda_{ e }, \lambda_{ He ^{++}}$ અને $\lambda_{ P }$ હોય તો ......View Solution
- 2બે બલ્બને $5\%$ ઊર્જા આપવામાં આવે તો તે દ્રશ્યમાન પ્રકાશની જેમ વર્તેં છે. $100$ વોટ ના લેમ્પ વડે પ્રતિ સેકન્ડે કેટલા કવોન્ટમ ઉત્સર્જાતા હશે? (દ્રશ્ય પ્રકાશની તરંગ લંબાઈ $5.6 \times10^{-5} cm$)View Solution
- 3સમાન ચુંબકીયક્ષેત્રમાં સમાન ત્રિજયામાં ભ્રમણ કરતાં $\alpha$-કણ અને પ્રોટોનની દ-બ્રોગ્લી તરંગલંબાઇનો ગુણોત્તર કેટલો થાય?View Solution
- 4સ્ફટીકના આંતર આણ્વીય સમતલો વચ્ચેનું મહતમ અંતર $10^{-7}\ cm$.છે. તો સ્ફટીક દ્વારા અભ્યાસ કરાતા ક્ષ-કિરણોની મહતમ તરંગલંબાઈ ........... $\mathop {\rm{A}}\limits^o $View Solution
- 5ફોટોઇલેક્ટ્રિક અસરના પ્રયોગમાં એક વિદ્યાર્થી સ્ટોપિંગ પોટેન્શિયલ $V_0$ નો તરંગલંબાઈ $\lambda $ ના વ્યસ્ત વિરુધ્ધનો આલેખ બે ધાતુ $A$ અને $B$ માટે દોરે છે, જે નીચે દર્શાવેલ છે. તેના માટે નીચેનામાંથી કયું વિધાન યોગ્ય સાબિત થશે?View Solution
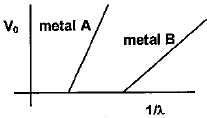
- 6ધાતુની સપાટી માટે ફોટોઇલેક્ટ્રિક વર્ક ફંક્શન $ 4.125 \;eV$ છે. આ સપાટી માટે કટ ઓફ તરંગલંબાઇનું મૂલ્ય ........... $\mathring A$ હશેView Solution
- 7ધાતુઓનું કાર્ય વિધેય $Na = 1.92 \,eV, K = 2.15 \,eV, Mo =4.17 \,eV, Ni = 5.0\, eV$ પ્રમાણે આપેલ છે.આ ધાતુઓ પૈકી કઈ ધાતુ $He - Cd$ લેસરમાંથી $3300 \,Å$ તરંગ લંબાઈના ઉત્સર્જન માટે ફોટો ઈલેક્ટ્રીક ઉત્સર્જન અપાતું નથી?View Solution
- 8એક ફોટોસંવેદી સપાટી પર $ I$ તીવ્રતાવાળું એકરંગી વિકિરણ આપાત કરવામાં આવે છે, ત્યારે ઉત્સર્જિત ફોટો ઇલેકટ્રોન્સની સંખ્યા અને તેમની મહત્તમ ગતિઊર્જા અનુક્રમે $N$ અને $K$ મળે છે. જો આપાત વિકિરણની તીવ્રતા $2I $ કરવામાં આવે,તો ઉત્સર્જિત ફોટો ઇલેકટ્રોન્સની સંખ્યા અને તેમની મહત્તમ ગતિઊર્જા અનુક્રમે કેટલી થશે?View Solution
- 9$1 \;MeV$ ઊર્જા ધરાવતા ફોટોનનું વેગમાન $kg m/s $ માં કેટલું થાય?View Solution
- 10$v$ ઝડપ સાથેના ઈલેક્ટ્રોન અને $c$ ઝડપ સાથેના ફોટોનની ડી-બ્રોગ્લી તરંગલંબાઈ સમાન છે. અનુક્રમે ઈલેક્ટ્રોનની ગતિઊર્જા $E _{ e }$ અને વેગમાન $P _{ e }$ અને ફોટોન માટે તે $E _{ ph }$ અને $p _{ ph }$ છે. નીંચેનામાંથી કયું વિધાન સાચું છે ?View Solution
