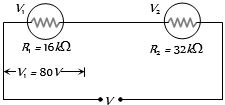
વોલ્ટમીટર $V_1$ અને $V_2$ ને $D.C.$ પરિપથમાં શ્રેણીમાં જોડેલ છે.$V_1$ નું અવલોકન $80\,V$ અને અવરોધ $200\,Ω/v$ છે.જો $V_2$ નો અવરોધ $32\,kΩ$ હોય,તો પરિપથનો કુલ વોલ્ટેજ કેટલા ............. $volts$ થાય?
Diffcult
d
(d) \({R_1} = 80 \times 200 = 16000\,\Omega = 16\,k\Omega \)
Current flowing through \({V_1}\)\(=\) Current flowing through \({V_2}\) \(=\) \(\frac{{80}}{{16 \times {{10}^3}}} = 5 \times {10^{ - 3}}\,A\).
So, potential differences across \({V_2}\) is
\({V_2} = 5 \times {10^{ - 3}} \times 32 \times {10^3} = 160\,{\rm{volt}}\)
Hence, line voltage \(V = {V_1} + {V_2} = 80 + 160 = 240\,V\).
(d) \({R_1} = 80 \times 200 = 16000\,\Omega = 16\,k\Omega \)
Current flowing through \({V_1}\)\(=\) Current flowing through \({V_2}\) \(=\) \(\frac{{80}}{{16 \times {{10}^3}}} = 5 \times {10^{ - 3}}\,A\).
So, potential differences across \({V_2}\) is
\({V_2} = 5 \times {10^{ - 3}} \times 32 \times {10^3} = 160\,{\rm{volt}}\)
Hence, line voltage \(V = {V_1} + {V_2} = 80 + 160 = 240\,V\).

Download our appand get started for free
Experience the future of education. Simply download our apps or reach out to us for more information. Let's shape the future of learning together!No signup needed.*
Similar Questions
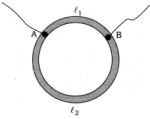
- 1એક રીંગ $R_0$ = $12\,\Omega$ અવરોધ ધરાવતા વાયરમાંથી બનાવેલ છે. તો $A$ અને $B$ બિંદુઓનું સ્થાન શોધો કે જેથી નીચે દર્શાવેલ પરીપથનો અવરોધ $8/3\,\Omega$ થી થાય.View Solution
- 2બલ્બને $(100\,W,200\,V)$ $160\,V$ ના પાવર સપ્લાય સાથે જોડવામાં આવે છે. કેટલો પાવર ($W$ માં) વપરાશે?View Solution
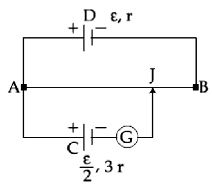
- 3$L$ લંબાઇનો અને $12\, r$ નો અવરોધ ધરાવતા એક પોટેન્શીયોમીટર તાર $AB$ અને $\varepsilon$ જેટલું $emf$ અને $r$ જેટલો આંતરિક અવરોધ ધરાવતા કોષ $D$ સાથે જોડવામાં આવે છે. $\varepsilon/2$ જેટલું $emf$ અને $3r$ જેટલો આતંરિક અવરોધ ધરાવતા કોષ $C$ ને આકૃતિમાં દર્શાવ્યા મુજબ જોડવામાં આવે છે. ગેલ્વેનોમીટરમાં દર્શાવતું શૂન્ય આવર્તન માટેની લંબાઈ $AJ$ _______ હશે.View Solution
- 4વિધાન $-1 :$ સ્વિચ $ON$ કરતી વખતે બલ્બ ફ્યુજ થવાની શક્યતા મહત્તમ હોય.View Solution
વિધાન $-2 : $ જ્યારે બલ્બ બંધ હોય ત્યારે તેનો અવરોધ બલ્બ ચાલુ ત્યારના અવરોધ કરતાં ઘણો નાનો હોય છે.
- 5જો વિદ્યુત પ્રવાહમાં $20 \%$ ઘટાડો કરવામાં આવે તો બલ્બના પ્રકાશની તીવ્રતામાં કેટલા ટકા ધટાડો થાય?View Solution
- 6$500\,W$ અને $200\,W$ ના બે બલ્બને $220\,V$ પર કામ કરી શકે છે.બંનેને સમાંતરમાાં જોડતા બંનેમાંથી ઉત્પન્ન થતી ઉષ્માનો ગુણોતર અને શ્નેણીમાં જોડતાં ઉત્પન્ન થતી ઉષ્માનો ગુણોતર કેટલો થાય?View Solution
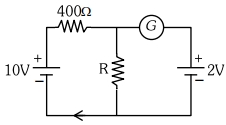
- 7જો પરિપથમાં ગેલ્વેનોમીટર $G$ કોઈ આવર્તન દર્શાવતુ ન હોય તો $R$નું મૂલ્ય $..........\,\Omega$ થાય.View Solution
- 8નીચેમાનો ક્યો આલેખ તાંબા માટે અવરોધકના ( $\rho$ ) નો તાપમાન $(T)$ સાથેનો બદલાવ દર્શાવે છે ?View Solution
- 9તારનો અવરોધ $50\,\Omega$ હોય તો $\log\,V$ અને $\log\,I$ વચ્ચેનો આલેખ........છે.View Solution
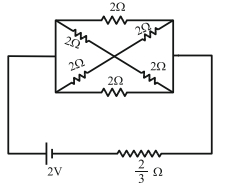
- 10નીચે દર્શાવેલ વિદ્યુત પરિપથમાં બેટરીનું emf $2 \mathrm{~V}$ અને આંતરિક અવરોધ $\frac{2}{3} \Omega$ છે. તો આ સંપૂર્ણ વિદ્યુત પરિપથમાં વપરાતો વિદ્યુત પાવર ...... $W$View Solution