$0.1\, kg$ દળ ધરાવતો કણ $0.1\, m$ ના કંપવિસ્તારથી સરળ આવર્તગતિ કરે છે. જ્યારે આ કણ સમતોલન સ્થાન પાસેથી પસાર થાય ત્યારે તેની ગતિઉર્જા $8\times10^{-3}\; Joule$ જેટલી છે. જો તેની શરૂઆતની કળા $45^o$ હોય તો તેની સરળ આવર્તગતિનું સમીકરણ શું થશે?.
AIIMS 2013,AIIMS 2017, Diffcult
a
The displacement of a particle in \(S.H.M.\) is given by
The displacement of a particle in \(S.H.M.\) is given by
\(y=a \sin (\omega t+\phi)\)
velocity \(=\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dt}}=\omega \mathrm{a} \cos (\omega \mathrm{t}+\phi)\)
The velocity is maximum when the particle passes through the mean position i.e...
\(\left(\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dt}}\right)_{\max }=\omega \mathrm{a}\)
The kinetic energy at this instant is given by
\(\frac{1}{2} \mathrm{m}\left(\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dt}}\right)_{\max }^{2}=\frac{1}{2} \mathrm{m} \omega^{2} \mathrm{a}^{2}=8 \times 10^{-3} \mathrm{joule}\)
\(\text { or } \quad \frac{1}{2} \times(0.1) \omega^{2} \times(0.1)^{2}=\)
\(8 \times 10^{-3}\)
Solving we get \(\omega=\pm 4\)
Substituting the values of a, \(\omega\) and \(\phi\) in the equation of \(S.H.M\)., we get
\(y=0.1 \sin (\pm 4 t+\pi / 4)\) metre
Download our appand get started for free
Experience the future of education. Simply download our apps or reach out to us for more information. Let's shape the future of learning together!No signup needed.*
Similar Questions
- 1સરળ આવર્ત ગતિ કરતાં પદાર્થની સ્થિતિઊર્જા સમતોલન સ્થાનથી કંપવિસ્તારના અડધા અંતરે $2.5\, J$ છે,તો કુલઊર્જા કેટલી .... $J$ થાય?View Solution
- 2એક કણ સીધી રેખામાં સરળ આવર્ત ગતિ કરે છે.તેની સ્થિર સ્થિતિમાંથી પહેલી $t$ $s$ માં તે $a$ જેટલું અંતર કાપે છે અને બીજી $t$ $s$ માં તે જ દિશામાં $2$ $a$ અંતર કાપે છે,તોView Solution
- 3$2 \,kg$ દળ ધરાવતો પદાર્થ $20 \,cm$ નાં કંપવિસ્તાર અને $1 \,s$ નાં આવર્તકાળથી સરળ આવર્ત ગતિ કરે છે. તેનો મહત્તમ વેગ ......... $m / s$ થશે.View Solution
- 4એક પદાર્થ ઉદગમથી શરૂ કરી $2\;s$ નાં આવર્તકાળથી સરળ આવર્ત દોલનો કરે છે. કેટલા સમય પછી તેની ગતિઊર્જા એ કુલ ઊર્જાના $75 \%$ જેટલી થશે ?View Solution
- 5$M$ અને $N$ સમાન દળના પદાર્થને અનુક્રમે $k_1$ અને $k_2$ બળ અચળાંક ધરાવતી દળરહિત સ્પ્રિંગ પર લટકાવેલ છે. જો દોલનો દરમિયાન તેમના મહત્તમ વેગ સમાન હોય, તો કંપવિસ્તારનો ગુણોત્તર કેટલો થાય?View Solution
- 6$m$ દળના લોલકને $l$ લંબાઇની દોરી વડે બાંધીને લટકાવતા તે $T$ આવર્તકાળથી સરળ આવર્ત ગતિ કરે છે. જો લોલકને લોલક કરતાં $\frac{1}{4}$ ગણી ઘનતા ધરાવતા પ્રવાહીમાં ડૂબાડીને દોરીની લંબાઈ મૂળ લંબાઈ કરતાં $1 / 3$ ગણી વધારવામાં આવે તો, સરળ આવર્ત ગતિનો આવર્તકાળ કેટલો થાય?View Solution
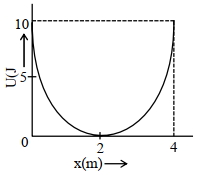
- 7$5\, {kg}$ દળને સ્પ્રિંગ સાથે જોડેલ છે. આ તંત્ર દ્વારા થતી સરળ આવર્તગતિની સ્થિતિઊર્જાનો ગ્રાફ આકૃતિમાં દર્શાવેલ છે. $4\, {m}$ લંબાઈના સાદા લોલકનો આવર્તકાળ સ્પ્રિંગતંત્રના આવર્તકાળ જેટલો જ છે. જ્યાં આ પ્રયોગ કરવામાં આવેલ છે તે ગ્રહ પર ગુરુત્વપ્રવેગનું મૂલ્ય (${m} / {s}^{2}$ માં) કેટલું હશે?View Solution
- 8એંજિનમાં રહેલ પિસ્ટન $7\, cm$ના કંપવિસ્તારથી શિરોલંબ સરળ આવર્ત ગતિ કરે છે.વોશર પિસ્ટનના ઉપરના ભાગમાં છે. મોટરની ઝડપમાં ધીમે ધીમે વધારો કરવામાં આવે છે. પિસ્ટનની આવૃતિ($Hz$ માં) કેટલી હોવી જોઈએ કે જેથી વોશર પિસ્ટન સાથે સંપર્કમાં રહે નહીં?View Solution
- 9એક $m$ દળના પદાર્થ પર $F$ બળ લગાવતા તે $F = - kx + {F_0}$ મુજબ સ્થાનાંતર કરે છે જો $k $ અને ${F_0}$ અચળાંક હોય તો કણ કેવી રીતે કંપન કરશે ?View Solution
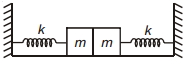
- 10View Solutionઆકૃતિનાં દર્શાવ્યા મુજબની જ પૃથ્વીની સપાટીને સમક્ષિતિજ રહે તેમ ગોઠવવામાં આવેલ છે. આ સ્થિતિમાં સ્પ્રિંગો પર કોઈ તણાવ નથી સામાન્ય સ્થિતિમાં છે. જો ડાબી તરફનું દળ ડાબી તરફ અને જમણી તરફનું દળ જમણી તરફ સરખા અંતેર ખેંચીને છોડવામાં આવે છે. જો પરિણામી અથડામણ સ્થિતિ સ્થાપક હોય તો આ પ્રણાલીના દોલનોનો આવર્તકાળ કેટલો હશે ?