$500\,W$ અને $200\,W$ ના બે બલ્બને $220\,V$ પર કામ કરી શકે છે.બંનેને સમાંતરમાાં જોડતા બંનેમાંથી ઉત્પન્ન થતી ઉષ્માનો ગુણોતર અને શ્નેણીમાં જોડતાં ઉત્પન્ન થતી ઉષ્માનો ગુણોતર કેટલો થાય?
Diffcult
a
(a) Resistance \({R_1}\) of \(500\, W\) bulb \( = \frac{{{{(220)}^2}}}{{500}}\)
Resistance \({R_2}\) of \(200\, W\) bulb \( = \frac{{{{(220)}^2}}}{{200}}\)
When joined in parallel, the potential difference across both the bulbs will be same.
Ratio of heat produced \( = \frac{{{V^2}/{R_1}}}{{{V^2}/{R_2}}} = \frac{{{R_2}}}{{{R_1}}} = \frac{5}{2}\)
When joined in series, the same current will flow through both the bulbs.
Ratio of heat produced \( = \frac{{{i^2}{R_1}}}{{{i^2}{R_2}}} = \frac{{{R_1}}}{{{R_2}}} = \frac{2}{5}\)
(a) Resistance \({R_1}\) of \(500\, W\) bulb \( = \frac{{{{(220)}^2}}}{{500}}\)
Resistance \({R_2}\) of \(200\, W\) bulb \( = \frac{{{{(220)}^2}}}{{200}}\)
When joined in parallel, the potential difference across both the bulbs will be same.
Ratio of heat produced \( = \frac{{{V^2}/{R_1}}}{{{V^2}/{R_2}}} = \frac{{{R_2}}}{{{R_1}}} = \frac{5}{2}\)
When joined in series, the same current will flow through both the bulbs.
Ratio of heat produced \( = \frac{{{i^2}{R_1}}}{{{i^2}{R_2}}} = \frac{{{R_1}}}{{{R_2}}} = \frac{2}{5}\)
Download our appand get started for free
Experience the future of education. Simply download our apps or reach out to us for more information. Let's shape the future of learning together!No signup needed.*
Similar Questions
- 1View Solutionવિધુતપ્રવાહ અને ડ્રિફટ વેગ વચ્ચે સંબંધ તારવો.
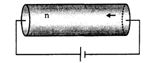
- 2$l$ લંબાઈના એક ધાતુના તારના બે છેડા વચ્ચેનો સ્થિતિમાનનો તફાવત $V$ મળે છે. જો......હોય તો ડ્રીફટ વેગ બમણો હશે.View Solution
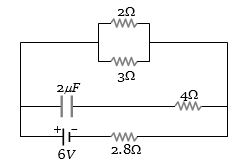
- 3આપેલ પરિપથમાં $2\,\Omega $ અવરોધમાંથી કેટલા .............. $A$ પ્રવાહ પસાર થાય?View Solution
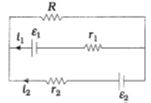
- 4View Solutionઆકૃતિમાં દર્શાવેલ વિદ્યુત પરિપથના સંદર્ભમાં નીચેનામાંથી કયું સમીકરણ સાચું છે?
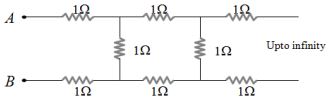
- 5આપેલ અનંત અવરોધ ધરાવતા પરીપથ માટે $A$ અને $B$ વચ્ચેનો અસરકારક અવરોધ કેટલો હશે ?View Solution
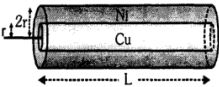
- 6$r$ ત્રિજ્યા અને '$ℓ$' લંબાઈના કોપરના તારને નિકલ પ્લેટ વડે આવરિત કરવામાં આવે છે જ્યાં સુધી તેની ત્રિજ્યા $2r$ બને. જો કોપર અને નિકલની અવરોધકતા $\rho_c$ અને $P_n$ હોય તો તારનો સમતુલ્ય અવરોધ શોધો.View Solution
- 7રૂમ તાપમાને એક તારનો અવરોધ $100\,\Omega $ છે જ્યારે તેને $220\,V$ સાથે જોડવામાં આવે ત્યારે તેમાથી $2\,A$ નો અચળ પ્રવાહ વહે છે અને તેનું તાપમાન રૂમના તાપમાન કરતાં $500\,^oC$ વધારે છે. તો આ તારની અવરોધકતાનો તાપમાન ગુણાંક કેટલો હશે?View Solution
- 8ધાતુના તારનો અવરોધ $35\, \Omega$ છે.તેને ખેંચીને લંબાઈ બમણી કરતાં નવો અવરોધ ($\Omega$ માં) કેટલો થશે?View Solution
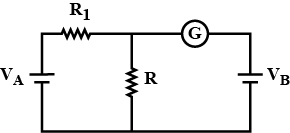
- 9આપેલ પરિપથમાં રહેલ કોષ $A$ અને $B$ નો અવરોધ નહિવત છે. $V _{ A }=12\; V , R _{1}=500\; \Omega$ અને $R =100\; \Omega$ માટે ગેલ્વેનોમીટર $(G)$ આવર્તન બતાવતું નથી તો $V_{B}$ નું મૂલ્ય .... $V$ હશેView Solution
- 10View Solutionઓહ્મના નિયમની આકૃતિ કઇ છે?
