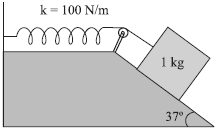
Mass of the block, \(m=1 kg\)
Spring constant, \(k=100 N m ^{-1}\)
Displacement in the block, \(x=10 cm =0.1 m\)
The given situation can be shown as in the following figure.
At equilibrium:
Normal reaction, \(R=m g \cos 37^{\circ}\)
Frictional force, \(f{=} \mu_{R}=m g \sin 37^{\circ}\)
Where, \(\mu\) is the coefficient of friction
Net force acting on the block \(=m g \sin 37^{\circ}-f\)
\(=m g \sin 37^{\circ}-\mu m g \cos 37^{\circ}\)
\(=m g\left(\sin 37^{\circ}-\mu \cos 37^{\circ}\right)\)
At equilibrium, the work done by the block is equal to the potential energy of the spring, i.e.,
\(m g\left(\sin 37^{\circ}-\mu \cos 37^{\circ}\right) x=\frac{1}{2} k x^{2}\)
\(1 \times 9.8\left(\sin 37^{\circ}-\mu \cos 37^{\circ}\right)=\frac{1}{2} \times 100 \times 0.1\)
\(0.602-\mu \times 0.799=0.510\)
\(\therefore \mu=\frac{0.092}{0.799}=0.115\)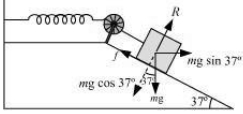
Download our appand get started for free
Similar Questions
- 1View Solutionએક દળ શિરોલંબ વર્તુળમય ગતિ કરે છે (આકૃતિ જુઓ). જો કણનો સરેરાશ વેગ વધારવામાં આવે, તો દોરી કયા બિંદુ આગળ તૂટશે?
- 2$a$ દળની ગોળી $ b$ વેગથી $c$ દળના બ્લોક સાથે અથડાઇને બ્લોકમાં સ્થિર થાય છે. તો બ્લોકનો વેગView Solution
- 3$1 \;kg $ દળવાળા પદાર્થને $20\; m/s$ જેટલા વેગથી ઊર્ધ્વ તરફ ફેંકવામાં આવે છે. પરિણામે તે $18\; m$ જેટલી ઊંચાઇ પ્રાપ્ત કર્યા બાદ ક્ષણ પૂરતો સ્થિર થાય છે. હવાના ઘર્ષણના કારણે ગુમાવતી ઊર્જા કેટલી ($J$ માં) હશે? ($g=10 \;ms^{-2}$)View Solution
- 4$L$ લંબાઈ દોરીના એક છેડે બાંધેલા પથ્થરને શિરોલંબ વર્તુળમાં ફેરવવામાં આવે જ્યાં દોરડાનો બીજો છેડો વર્તુળની મધ્યમાં છે. કોઈ એક સમયે પથ્થર સૌથી નીચા બિંદુએ છે અને તેનો વેગ $u$ છે. જ્યારે દોરીની સ્થિતિ સમક્ષિતિજ થાય, ત્યારે તેના વેગમાં થતાં ફેરફારનું મૂલ્ય કેટલું હશે?View Solution
- 5View Solutionવિધાન: સ્પ્રિંગની સ્થિતિઉર્જા વિરુદ્ધ સ્પ્રિંગનું ખેંચાણ અથવા દબાણ નો આલેખ સુરેખા મળે.
કારણ: ખેંચાયેલી કે દબાયેલી સ્પ્રિંગની સ્થિતિઉર્જા એ ખેંચાણ કે દબાણ ના વર્ગના સમપ્રમાણ માં હોય.
- 6એક માણસ પોતાની ઝડપમાં $4 m/s$ નો વધારો કરતાં તેની ગતિઊર્જા બમણી થાય છે, તો તેની મૂળ ઝડપ કેટલી હશે?View Solution
- 7View Solutionવિધાન: હેલિકોપ્ટર માં ફરજિયાતપણે બે પંખીયા તો હોવા જ જોઈએ.
કારણ: બંને પંખીયા હેલિકોપ્ટરનું રેખીય વેગમાન સંરક્ષે છે.
- 8એક કણ સમતલમાં $\overrightarrow{ F }=\left(4 x \hat{i}+3 y^{2} \hat{j}\right)$ જેટલું ચલ બળ અનુભવે છે. અંતર મીટરમાં અને બળ ન્યૂટનમાં છે તેમ ધારો. જો કણ $x-y$ સમતલમાં બિંદૂ $(1,2)$ થી $(2,3)$ આગળ ખસે તો ગતિઉર્જા...........$J$ જેટલી બદલાશે.View Solution
- 9એક ગોળીનું વજન $10 \,g$ છે અને તે $300 \,m / s$ વેગ એક $5 \,kg$ બરફના બ્લોકને અથડાઈને અટકી જાય છે. બરફનો બ્લોક એક લીસી સપાટી પર છે. તો અથડામણ પછીને બ્લોકની ઝડપ .............. $cm / s$ છે.View Solution
- 10$M $ દળનો બ્લોક $ K$ બળ અચળાંક ધરાવતી સ્પિંગ્ર સાથે અથડાવાથી સ્પિંગ્રનું સંકોચન $ L$ થાય છે.તો બ્લોકનું અથડામણ પછીનું મહત્તમ વેગમાન કેટલું થાય?View Solution

