$G$ અવરોધ ધરાવતતું ચલિત ગુચળાવાળું ગેલ્વેનોમીટર $I_g$ પ્રવાહ માટે પૂર્ણ આવર્તન દર્શાવે છે.આ ગેલ્વેનોમીટરને $(i)$ $R_A$ જેટલો શંટ અવરોધ જોડીને $0$ થી $I_0 (I_0 > I_g)$ માપી શકતા એમીટરમા $(ii)$ $R_V$ અવરોધ શ્રેણીમાં જોડી $0$ થી $V(V = GI_0)$ વૉલ્ટ માપી શકતા વોલ્ટમીટરમાં ફેરવેલ હોય તો ...
JEE MAIN 2019, Diffcult
b
When galvanometer is used an ammeter shunt is used in parallel with galvanometer.
When galvanometer is used an ammeter shunt is used in parallel with galvanometer.
\(\therefore \quad \mathrm{I}_{g} \mathrm{G}=\left(\mathrm{I}_{0}-\mathrm{I}_{g}\right) \mathrm{R}_{\mathrm{A}}\)
\(\therefore \quad R_{A}=\left(\frac{I_{g}}{I_{0}-I_{g}}\right) G\)
When galvanometer is used as a voltmeter, resistance is used in series with galvanometer.
\(\mathrm{I}_{g}\left(\mathrm{G}+\mathrm{R}_{\mathrm{v}}\right)=\mathrm{V}=\mathrm{GI}_{0}\left(\text { given } \mathrm{V}=\mathrm{GI}_{0}\right)\)
\(\therefore R_{v}=\frac{\left(I_{0}-I_{g}\right) G}{I_{g}}\)
\(\therefore \quad {{\text{R}}_{\text{A}}}{{\text{R}}_{\text{v}}} = {{\text{G}}^2}\& \frac{{{{\text{R}}_{\text{A}}}}}{{{{\text{R}}_{\text{v}}}}} = {\left( {\frac{{{{\text{I}}_g}}}{{{{\text{I}}_0} - {{\text{I}}_g}}}} \right)^2}\)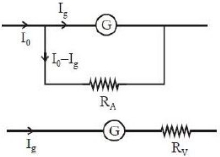
Download our appand get started for free
Experience the future of education. Simply download our apps or reach out to us for more information. Let's shape the future of learning together!No signup needed.*
Similar Questions
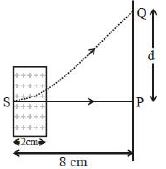
- 1આકૃતિમાં દર્શાવ્યા પ્રમાણે એક $x-$ અક્ષ પર $100\, eV$ ઉર્જાથી ગતિ કરતો ઈલેક્ટ્રોન $\vec B = (1.5\times10^{-3}T)\hat k$ જેટલા ચુંબકીય ક્ષેત્રમાં $S$ આગળથી દાખલ થાય છે.ચુંબકીય ક્ષેત્ર $x = 0$ અને $x = 2\, cm$ વચ્ચે પ્રવર્તે છે.$S$ બિંદુથી $8\, cm$ દૂરના પડદા પર $Q$ બિંદુ આગળ ઇલેક્ટ્રોન નોંધાય છે તો $P$ અને $Q$ વચ્ચેનું અંતર $d$ .....$cm$ હશે?View Solution
- 2$5\,cm,12\,cm$ અને $13\,cm$ બાજુઓ ધરાવતી કાટકોણ ત્રિકોણાકારની એક આંટાની પ્રવાહલૂપ $2\,A$ નો પ્રવાહ ધારણ કરે છે. આ લૂપ $0.75\,T$ મૂલ્ચના સમાન ચુંબકીયક્ષેત્રમાં લૂપની $13\,cm$ વાળી બાજુની સમાંતર દિશામાં મૂકવામાં આવે છે. $5\,cm$ ની બાજુ પર ચુંબકીય બળનું મૂલ્ય $\frac{x}{130}\,N$ છે. તો $x$ નું મૂલ્ય $...........$ છે.View Solution
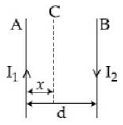
- 3આકૃતિમાં દર્શાવ્યા પ્રમાણે $d$ અંતરે રહેલ બે તાર $A$ અને $B$ માથી $I_1$ અને $I_2$ પ્રવાહ પસાર થાય છે.$A$ ને સમાંતર અને $A$ થી $x$ અંતરે $I$ પ્રવાહ પસાર થતો ત્રીજો તાર $C$ એવી રીતે મૂકવામાં આવે છે કે જેથી તેના પર લાગતું પરિણામી બળ શૂન્ય થાય. તો $x$ ની શક્ય કિમત .....View Solution
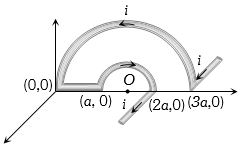
- 4આપેલ પરિપથમાં કેન્દ્ર $O$ પર ચુંબકીયક્ષેત્ર કેટલું થાય?View Solution
- 5$200$ આંટાની સંખ્યા, $2.5 \times 10^{-4} \mathrm{~m}^2$ નું ક્ષેત્રફળ અને $100 \mu \mathrm{A}$ પ્રવાહ ધરાવતા એક વર્તુળાકર ગૂંચળાન જ્યારે $1 \mathrm{~T}$ જેટલા નિયમિત ચુંબકીય ક્ષેત્રમાં મૂકવામાં આવે છે.ત્યારે તેની પ્રારંભિક સ્થિતિમાંથી $90^{\circ}$ એ એવી રીતે ભ્રમણ કરવામાં આવે છે કે જેની $\vec{M}$ એ $\vec{B}$ ને લંબ થાય તે માટે કેરવું પડતું જરૂરી કાર્ય. . . . . $\mu \mathrm{J}$ હશે.View Solution
- 6ગેલ્વેનોમીટરનો અવરોધ $R$ છે.પ્રવાહક્ષમતા ચાર ગણો કરવા કેટલા શંટની જરૂર પડે?View Solution
- 7$-2\;\mu C\;$ વિદ્યુતભાર ધરાવતો કણ $2\;T$ ચુંબકીયક્ષેત્રમાં $y$ દિશામાં દાખલ થાય, જ્યારે તેનો વેગ $\left( {2\hat i + 3\hat j} \right) \times \;{10^6}\,m/s$ ત્યારે તેના પર લાગતું ચુંબકીય બળ .....View Solution
- 8ઇલેકટ્રોનને જયારે $V$ વોલ્ટથી પ્રવેગીત કરીને ચુંબકીયક્ષેત્રમાં દાખલ કરવામાં આવે ત્યારે તેના પર બળ $F$ .લાગે છે.જયારે ઇલેકટ્રોનને $5\,V $ વોલ્ટથી પ્રવેગીત કરીને ચુંબકીયક્ષેત્રમાં દાખલ કરવામાં આવે ત્યારે તેના પર કેટલું બળ લાગશે?View Solution
- 9View Solutionએકબીજાને સમાંતર રહેલા વિદ્યુતતંત્ર અને ચુંબકીયક્ષેત્રમાં સ્થિર વિદ્યુતભારિત કણ મુક્તા તેનો ગતિપથ ....
- 10$30$ કાપા ધરાવતા ગેલ્વેનોમીટરની વિધુતપ્રવાહ સંવેદીતા $20$ $\mu A$ કાપા. ક્રમની છે. તેનો અવરોધ $25\,\Omega$ નો છે. આ એમિટરને $1$ વોલ્ટના વોલ્ટમીટર કેવી રીતે ફેરવશો ............. $\Omega$View Solution
