What is Ohm’s law? Explain how it is used to define the unit of resistance.
Ohm’s law gives a relationship between current (I) and potential difference (V). According to ohm’s law: At constant temperature, the current flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to the potential difference across its ends. If I is the current flowing through a conductor and V is the p.d. across its ends, then according
to the ohm’s law:
$\text{I}\propto\text{V}$
or, $\text{I}\propto\text{V}$
or, V = RI
or, $\text{R}=\frac{\text{V}}{\text{I}}$
where, R is a constant called ''resistance'' of the conductor.
The unit of resistance is ohm.
If V = 1 volt and I = 1 amp, then $\text{R}=\frac{1}{1}=1\text{ohm}$
Thus, 1 ohm is the resistance of a conductor such that when a potential difference of 1 volt is applied to its ends, a current of 1 amp flows through it.
to the ohm’s law:
$\text{I}\propto\text{V}$
or, $\text{I}\propto\text{V}$
or, V = RI
or, $\text{R}=\frac{\text{V}}{\text{I}}$
where, R is a constant called ''resistance'' of the conductor.
The unit of resistance is ohm.
If V = 1 volt and I = 1 amp, then $\text{R}=\frac{1}{1}=1\text{ohm}$
Thus, 1 ohm is the resistance of a conductor such that when a potential difference of 1 volt is applied to its ends, a current of 1 amp flows through it.
Download our appand get started for free
Experience the future of education. Simply download our apps or reach out to us for more information. Let's shape the future of learning together!No signup needed.*
Similar Questions
- 1A flash of lightning carries $10\ C$ of charge which flows for $0.01\ s$. What is the current? If the voltage is $10MV$, what is the energy?View Solution
- 2Calculate the area of cross-section of a wire if its length is 1.0m, its resistance is $23 Ω$ and the resistivity of the material of the wire is $1.84\times10 Ω\ \text{m}.$View Solution
- 3Calculate the resistance of an aluminium cable of length $10\ km$ and diameter $2.0\ mm$ if the resistivity of aluminium is $2.7\times10 Ω\ \text{m}.$View Solution
- 4View SolutionWhat is the resistance between A and B in the figure given below?
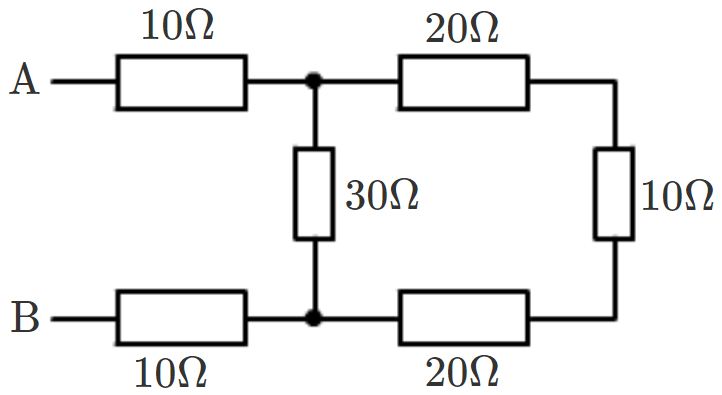
- 5The electrical resistivities of four materials $A, B, C$ and $D$ are given below:View Solution
$\text{A}\ -110\times10^{-8}\Omega\text{ m}$
$\text{B}-\ 1.0\times10^{10}\Omega\text{ m}$
$\text{C}-\ 10.0\times10^{-8}\Omega\text{ m}$
$\text{D}-\ 2.3\times10^{3}\Omega\text{ m}$
Which material is:- Good conductor.
- Resistor.
- Insulator, and
- Semiconductor
- 6View SolutionGive three reasons why different electrical appliances in a domestic circuit are connected in parallel.
- 7You are given one hundred $1 \Omega $ resister. What is the smallest and largest resistance you can make in a circuit using these?View Solution
- 8What possible values of resultant resistance one can get by combining two resistances, one of value $2$ ohm and the other $6$ ohm?View Solution
- 9A wire is 1.0m long, 0.2mm in diameter and has a resistance of $10Ω.$ Calculate the resistivity of its material?View Solution
- 10For the circuit shown in the diagram below:View Solution
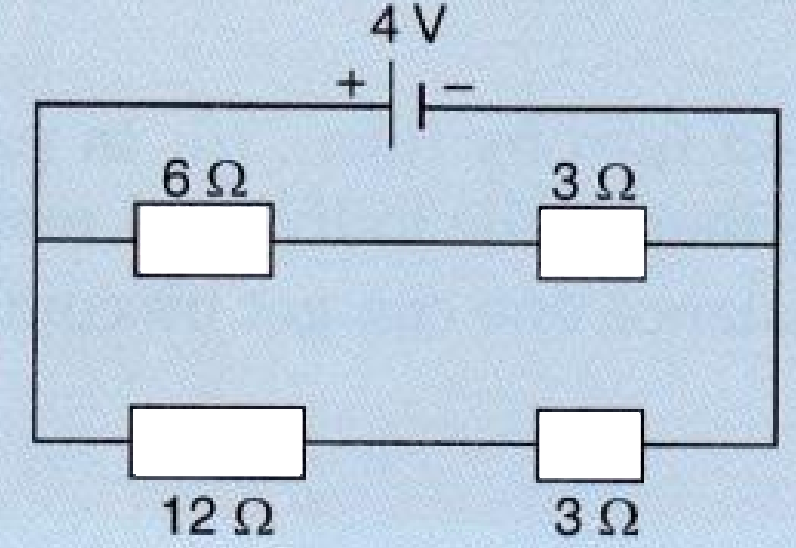
What is the value of :
Current through $6 Ω$ resistor?
Potential difference across $12 Ω$ resistor?
