Kinetic energy of a charged particle,
\(K=\frac{1}{2} m v^{2} \text { or } v=\sqrt{\frac{2 K}{m}}\)
Radius of the circular path of a charged particle in uniform magnetic field is given by
\(R=\frac{m v}{B q}=\frac{m}{B q} \sqrt{\frac{2 K}{m}}=\frac{\sqrt{2 m K}}{B q}\)
Mass of a proton, \(m_{p}=m\)
Mass of an \(\alpha\) -particle, \(m_{\alpha}=4 m\)
Charge of a proton, \(q_{p}=e\)
Charge of an \(\alpha\) -particle, \(q_{\alpha}=2 e\)
\(\therefore \quad R_{p}=\frac{\sqrt{2 m_{p} K_{p}}}{B q_{p}}=\frac{\sqrt{2 m K_{p}}}{B e}\)
and \(R_{\alpha}=\frac{\sqrt{2 m_{\alpha} K_{\alpha}}}{B q_{\alpha}}=\frac{\sqrt{2(4 m) K_{\alpha}}}{B(2 e)}=\frac{\sqrt{2 m K_{\alpha}}}{B e}\)
\(\therefore \quad \frac{R_{p}}{R_{\alpha}}=\sqrt{\frac{K_{p}}{K_{\alpha}}}\)
As \(R_{p}=R_{\alpha}\) (given) \(\therefore K_{\alpha}=K_{p}=1\, \mathrm{MeV}\)
Download our appand get started for free
Similar Questions
- 1View Solutionકોઈ વિસ્તારમાં નિયમિત વિદ્યુતક્ષેત્ર અને નિયમિત ચુંબકીયક્ષેત્ર એક જ દિશામાં છે. જો આ વિસ્તારમાં ઇલેકટ્રોનને અમુક વેગથી ક્ષેત્રની દિશામાં ગતિ કરાવતાં ઇલેકટ્રોન ....
- 2$1000$ આંટા ધરાવતી કોઇલની સરેરાશ ત્રિજ્યા $62.8\,cm$ છે. જો કોઇલના તાર દ્વારા વહન થતો પ્રવાહ $1\,A$ હોય, તો કોઇલના કેન્દ્રમાં ઉત્પન્ન થતા ચુંબકીય ક્ષેત્રનું મૂલ્ય લગભગ કેટલું હશે? (મુક્ત અવકાશની પરમીએબીલીટી $=4 \pi \times 10^{-7}\, H / m$)View Solution
- 3એક ગજીયા ચુંબક માટે ચુંબકીય ચાકમાત્રા $0.5 \mathrm{Am}^2$ છે. તેને $8 \times 10^{-2} \mathrm{~T}$ ધરાવતા સમાન (નિયમિત) ચુંબકીયક્ષેત્રમાં લટકાવવામાં આવે છે. તેની સૌથી સ્થાય (સ્થિર) સ્થિતિમાંથી સૌથી અસ્થિર સ્થિતિમાં ભ્રમણ કરાવવા કરવું પડતું કાર્ય. . . . . . . . . થશે.View Solution
- 4એક અવાહક પાતળા $l$ લંબાઇના સળીયા પર $\rho \left( x \right) = {\rho _0}\,\frac{x}{l}$ જેટલી રેખીય વિજભાર ઘનતા છે. ઉગમ બિંદુ $(x= 0)$ માંથી પસાર થતી અને સળીયાને લંબ અક્ષને અનુલક્ષીને સળિયાને પરિભ્રમણ કરાવવામાં આવે છે. જો સળીયો $n$ પરિભ્રમણ પ્રતિ સેકન્ડ ફરતો હોય તો સળીયા માટે સમય સરેરાશ ચુંબકીય ચાક માત્રા કેટલી હશે?View Solution
- 5કોઈ વિસ્તારમાં ચુંબકીય ક્ષેત્ર $\overrightarrow{ B }=(\hat{i}+3 \hat{j}+4 \hat{k}) \;\mu T$ અને વિદ્યુતક્ષેત્ર $\overrightarrow{ E }=10 \hat{ i } \;\mu V / m$ છે.તેમાં પ્રોટોન $\overrightarrow{ V }=2 \hat{ i }$ થી દાખલ થાય તો તેનો પરિણમી કુલ પ્રવેગ ($m / s ^{2}$ માં) કેટલો થશે?View Solution
- 6$0.01\,{m^2}$ ક્ષેત્રફળ ધરાવતા વર્તુળાકાર લૂપમાંથી $10\;A$ નો પ્રવાહ વહે છે, જેને $0.1\,T$ ચુંબકીયક્ષેત્રમાં લંબરૂપે ગોઠવેલ છે. લૂપ પર લાગતું ટોર્ક ($N-m$ માં) કેટલું હશે?View Solution
- 7$3\, cm$ ત્રિજયા ધરાવતી પ્રવાહધારિત રીંગની અક્ષ પર $4\, cm$ અંતરે ચુંબકીયક્ષેત્ર $54 \,\mu T$ છે,તો કેન્દ્ર પર ચુંબકીયક્ષેત્ર કેટલા ......$\mu T$ થાય?View Solution
- 8$10\,A$ વીજપ્રવાહ ધારિત બે લાંબા સુરેખ વાહક તારને $5\,cm$ અંતરે એકબીજાને સમાંતર રાખેલ છે. તાર $1$ ની $10\,cm$ લંબાઈ પર લાગતા ચુંબકીયક્ષેત્રનું, મૂલ્ય $F_1$ છે. જો બંને તાર વચ્ચેનું અંતર અડધું, કરવામાં આવે અને તેમાંથી વહેતા પ્રવાહ બમણા કરવામાં આવે, તો તાર $1$ ની $10\,cm$ લંબાઈ પર લાગતું બળ $F_2$ કેટલું થાય ?View Solution
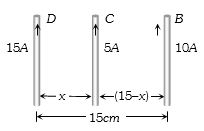
- 9આપેલ તંત્રમાં તાર $C$ બળ અનુભવતું ન હોય,તો $x$ નું મૂલ્ય કેટલું હોવું જોઈએ?View Solution
- 10એક વિસ્તારમાં એકબીજાને લંબરૂપે $20\; Vm ^{-1}$ જેટલું વિદ્યુતક્ષેત્ર અને $0.5\;T$ ચુંબકીયક્ષેત્ર બંને પ્રવર્તે છે. તેમાં એક ઇલેકટ્રોન બંનેને લંબરૂપે અચળ વેગથી ગતિ કરતો હોય, તો તેનો વેગ કેટલો હશે?View Solution
