According to Ohm's Law, \(I\) \(=\frac{V}{R}\)
\(\mathrm{I}_{\mathrm{g}}=\frac{\mathrm{V}}{\mathrm{R}+\mathrm{G}}\)
where, \(I \)\(_{g}\) - Galvanometer current, \(G-\)Galvonometer resistance
When shunt of resistance \(S\) is connected parallel to the Galvanometer then
\(\mathrm{G}=\frac{\mathrm{GS}}{\mathrm{G}+\mathrm{S}}\)
\(\therefore I=\frac{V}{R+\frac{G S}{G+S}}\)
Equal potential difference is given by
\(\mathrm{I}_{\mathrm{g}}^{\prime} \mathrm{G}=\left(\mathrm{I}-\mathrm{I}_{\mathrm{B}}^{\prime}\right) \mathrm{S}\)
\(\mathrm{I}_{\mathrm{g}}^{\prime}(\mathrm{G}+\mathrm{S})=\mathrm{IS}\)
\(\Rightarrow \frac{\mathrm{I}_{\mathrm{g}}}{2}=\frac{\mathrm{IS}}{\mathrm{G}+\mathrm{S}}\)
\(\Rightarrow \frac{\mathrm{v}}{2(\mathrm{R}+\mathrm{G})}=\frac{\mathrm{v}}{\mathrm{R}+\frac{\mathrm{GS}}{\mathrm{G}+\mathrm{S}}} \times \frac{\mathrm{S}}{\mathrm{G}+\mathrm{S}}\)
\( \Rightarrow \frac{1}{{2(R + G)}} = \frac{S}{{R(G + S) + GS}}\)
\(\Rightarrow R(G+S)+G S=2 S(R+G)\)
\(\Rightarrow \mathrm{RG}+\mathrm{RS}+\mathrm{GS}=2 \mathrm{S}(\mathrm{R}+\mathrm{G})\)
\(\Rightarrow \mathrm{RG}=2 \mathrm{S}(\mathrm{R}+\mathrm{G})-\mathrm{S}(\mathrm{R}+\mathrm{G})\)
\(\therefore \mathrm{RG}=\mathrm{S}(\mathrm{R}+\mathrm{G})\)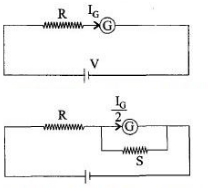
Download our appand get started for free
Similar Questions
- 1$1000$ આંટા પ્રતિ મીટર ધરાવતા સોલેનોઇડની સાપેક્ષ પરમીએબિલિટી $500$ છે. સોલેનોઇડના ગૂચળામાંથી $5\, A$ નો પ્રવાહ વહેતો હોય તો સોલેનોઇડમાંથી ઉત્પન્ન થતું ચુંબકીયક્ષેત્ર કેટલું હશે?View Solution
$\left(\mu_0=4 \pi \times 10^{-7} H / m \right)$
- 2$4.0\, cm$ અંતરે રહેલા, બે લાંબા સીધા અને સમાંતર તાર $A$ અને $B$ માંથી $8.0 \,A$ અને $5.0\, A$ વિદ્યુતપ્રવાહો એક જ (સમાન) દિશામાં વહે છે. તાર ના $10 \,cm$ લંબાઈના વિભાગ પર લાગતું બળ શોધોView Solution
- 3$12\, A$ પ્રવાહધારીત તારથી કેટલા અંતરે ચુંબકીયક્ષેત્ર $3 \times 10^{-5} Wb / m ^{2}$ થાય?View Solution
- 4$4 \pi$ મીટર લંબાઈના તારને વાળીને $6$ બાજુઓ વાળો બહુકોણ (ષટ્કોણ) બનાવવામાં આવે છે. જો બહુકોણ $4 \pi \sqrt{3} \mathrm{~A}$ વિદ્યુત્પવાહનું વહન કરતો હોય તો બહુકોણના કેન્દ્ર પરનું ચુંબકીય ક્ષેત્ર $10^{-7} x$ ટેસ્લા છે. $x$ નું મૂલ્ય____________છે.View Solution
- 5સ્પેક્ટ્રોમીટરથી આયનનું દળ માપવામાં આવે છે,વિદ્યુતસ્થિતિમાન $V$ દ્વારા પ્રવેગિત કરતાં તે $R$ ત્રિજ્યામાં $B$ ચુંબકીયક્ષેત્રમાં વર્તુળમય ગતિ કરે છે.જો $V$ અને $B$ અચળ રાખવામાં આવે તો (આયન પર વિદ્યુતભાર $/$ આયનના દળ) કોનાં સમપ્રમાણમાં હોય.View Solution
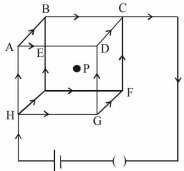
- 6આકૃતિ મુજબ $d$ જેટલી સમાન લંબાઈ એ સમાન અવરોધ ધરાવતા વાયરોથી એક ધન બનાવવામાં આવેલ છે અને તેમાં સ્થિર પ્રવાહ પસાર થાય છે. આ રચનાના કારણે તેના કેન્દ્ર $p$ માં ચુંબકીય ક્ષેત્ર શું હશે?View Solution
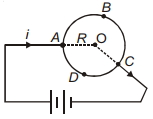
- 7એક એેકરૂપ વર્તુળાકાર રીંગને બેટરીના છેડા સાથે જોડેલ છે.તારના $A B C$ ભાગને લીધે કેન્દ્ર પાસે ચુંબકીયક્ષેત્ર પ્રેરણ કેટલુ હશે? ($ABC$ની સંજ્ઞા, $=I_1$ ની $A D C$ લંબાઈ $\left.=I_2\right)$View Solution
- 8$1 \Omega$ નો અવરોધ, $2 \times 10^{-6} \Omega \mathrm{m}$, ની અવરોધક્તા, $10 \mathrm{~mm}^2$ નું આડછેદનું ક્ષેત્રફળ અને $500 \mathrm{~g}$ દળ ધરાવતા એક ધાતુના સીધા તારમાંથી $2 A$ પ્રવાહ પસાર થાય છે. તેને નિયમિત ચુંબકીય ક્ષેત્ર $\vec{B}$ ની મદદથી હવામાં મધ્યમાં સમક્ષિતિજ રીતે લટકવવામાં આવે છે. $B$ નું મૂલ્ય. . . . . . . . . $\times 10^{-1} \mathrm{~T}$ છે. $\left(\mathrm{g}=10 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}^2\right.$ છે. )View Solution
- 9View Solutionચલિત ગુંચળાવાથા ગેલ્વેનોમીટરમાં ફોસ્ફર બ્રોન્ઝ પટ્ટીનો ઉપયોગ થાય છે,કારણ કે
- 10$v$ વેગથી ગતિ કરતા $q$ વિદ્યુતભાર પર લાગતું સ્થિત વિદ્યુતકીય બળ $\left(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{F}_1}\right)$ અને ચુંબકીય બળ $\left(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{F}_2}\right)$ ને. . . . . . . .રીતે લખી શકાય.View Solution
