A p.d. of 6V is applied to two resistors of $3 Ω$ and $6 Ω$ connected in parallel. Calculate:
The combined resistance.
The current flowing in the main circuit.
The current flowing in the $3 Ω$ resistor.
The combined resistance.
The current flowing in the main circuit.
The current flowing in the $3 Ω$ resistor.
$V = 6V,$
$R_1 = 3 ohm$, $R_2 = 6\ ohm$ (in parallel)
Combined resistance, $\frac{1}{\text{R}}=\frac{1}{\text{R}_1}+\frac{1}{\text{R}_2}$
$\frac{1}{\text{R}}=\frac{1}{3}+\frac{1}{6}=\frac{3}{6}=\frac{1}{2}$
R = 2 ohm
Current flowing in the main circuit, $\text{I}=\frac{\text{V}}{\text{R}}=\frac{6}{2}=3\text{A}$
Current flowing in 3 ohm resistor $=\frac{\text{V}}{\text{R}_1}=\frac{6}{3}=2\text{A}$
$R_1 = 3 ohm$, $R_2 = 6\ ohm$ (in parallel)
Combined resistance, $\frac{1}{\text{R}}=\frac{1}{\text{R}_1}+\frac{1}{\text{R}_2}$
$\frac{1}{\text{R}}=\frac{1}{3}+\frac{1}{6}=\frac{3}{6}=\frac{1}{2}$
R = 2 ohm
Current flowing in the main circuit, $\text{I}=\frac{\text{V}}{\text{R}}=\frac{6}{2}=3\text{A}$
Current flowing in 3 ohm resistor $=\frac{\text{V}}{\text{R}_1}=\frac{6}{3}=2\text{A}$
Download our appand get started for free
Experience the future of education. Simply download our apps or reach out to us for more information. Let's shape the future of learning together!No signup needed.*
Similar Questions
- 1View SolutionHow much energy is consumed when a current of 5 amperes flows through the filament (or element) of a heater having resistance of 100 ohms for two hours? Express it in joules.
- 2Calculate the resistance of an aluminium cable of length $10\ km$ and diameter $2.0\ mm$ if the resistivity of aluminium is $2.7\times10 Ω\ \text{m}.$View Solution
- 3View SolutionTen bulbs are connected in a series circuit to a power supply line. Ten identical bulbs are connected in a Parallel circuit to an identical power supply line.
- Which circuit would have the highest voltage across each bulb?
- In which circuit would the bulbs be brighter?
- In which circuit, if one bulb blows out, all others will stop glowing
- Which circuit would have less current in it?
- 4View SolutionCalculate the cost of operating a heater of 500W for 20hours at the rate of? ₹3.90 per unit.
- 5View SolutionWhat is a voltmeter? How is a voltmeter connected in the circuit to measure the potential difference between two points. Explain with the help of a diagram.
- 6In the circuit shown below, the voltmeter reads $10V.$View Solution
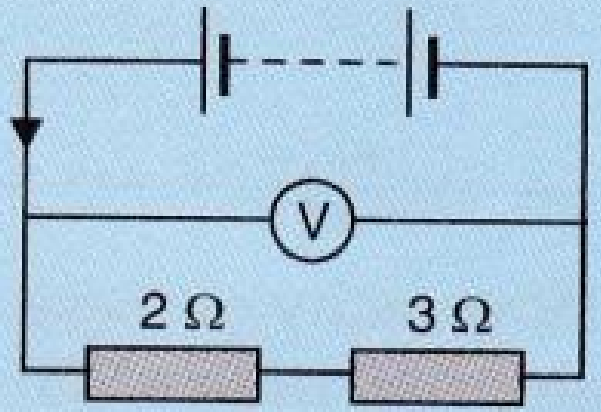
- What is the combined resistance?
- What current flows?
- What is the p.d. across $ 2 Ω$ resistor?
- What is the p.d. across $3 Ω$ resistor?
- 7Calculate the work done in moving a charge of $4$ coulombs from a point at $220$ volts to another point at $230$ volts.View Solution
- 8View SolutionConsider the circuit given below where A, B and C are three identical light bulbs of constant resistance.
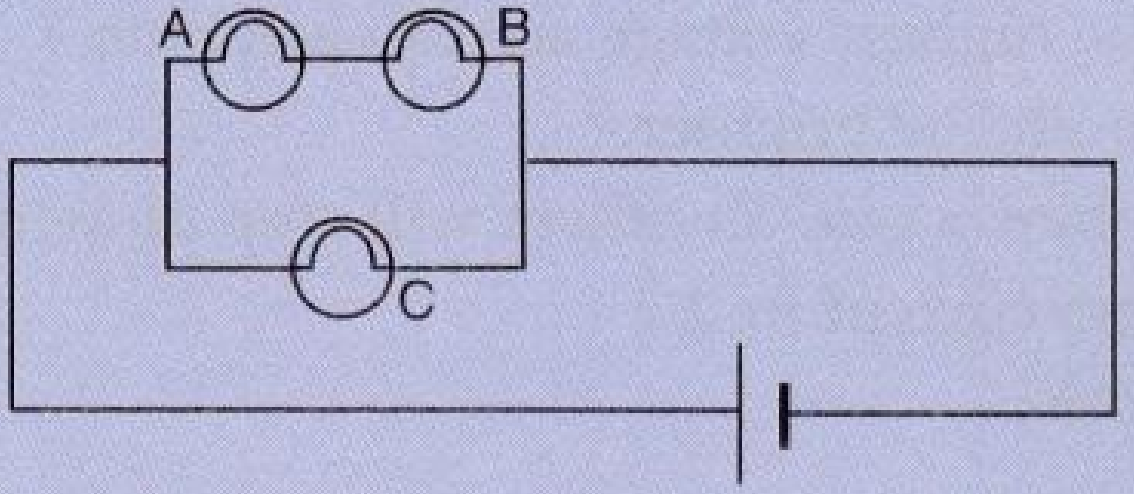
- List the bulbs in order of increasing brightness.
- If C burns out, what will be the brightness of A now compared with before?
- If B burns out instead, what will be the brightness of A and C compared with before?
- 9View SolutionA p.d. of 10V is needed to make a current of 0.02A flow through a wire. What p.d. is needed to make a current of 250mA flow through the same wire?
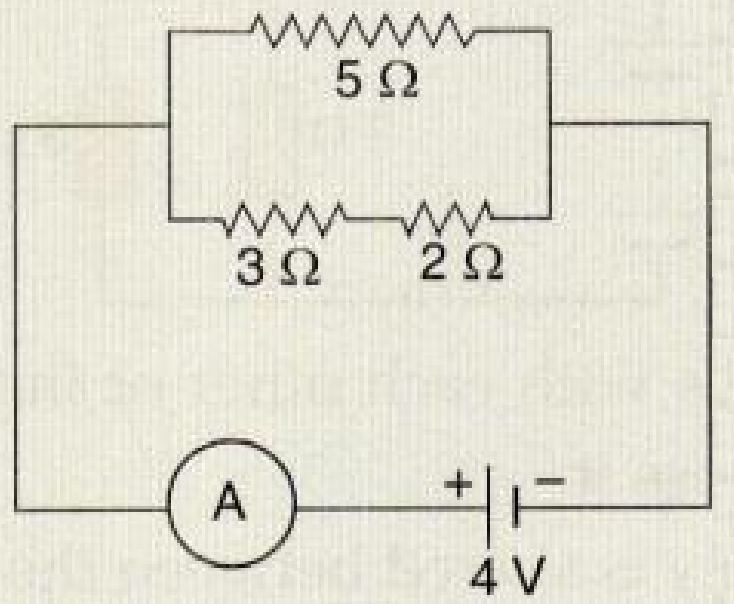
- 10With the help of a circuit diagram, obtain the relation for the equivalent resistance of two resistances connected in parallel. In the circuit diagram shown below, find:View Solution
- Total resistance.
- Current shown by the ammeter $A$